Microsoft's 365 Component, OneDrive cloud storage service is a huge convenience because it keeps your files synced across devices and backed up onto the internet. Since both OneDrive and Teams are using SharePoint as their backend to store files, it is quite confusing when to use OneDrive, Teams and SharePoint when starting to store your files. Here are some clarification for this question based on what I understand.
Since Blob storage also could be an option for sharing with external users. I will add it into this post to discuss too.Considerations:
- External sharing configuration
- User Experience
- Governance
Recommended Settings for OneDrive/SharePoint External File Sharing
SharePoint has external sharing settings at both the organization level and the site level.
Best practice:
- If you have confidential information that should never be shared externally, we recommend storing the information in a site that has external sharing turned off. Create additional sites as needed to use for external sharing. This helps you to manage security risk by preventing external access to sensitive information
- Limit accidental exposure to files when sharing with people outside your organization
- Turn Off Anyone Links at organization level or Turn off for a site
- Domain filtering
- Limit external sharing function to specified security groups
- If you have to turn on Anyone Links, here are some best practices for sharing files and folders with unauthenticated users
- Set an expiration date for anyone links, either at Organization-level or a site level
- Set link permissions to restricited level such as View.
- Set default link type to only work for people in your organization, By default, Anyone sharing set set to Anyone. You can set it up at Organization-level or a site level.
- Prevent unauthenticated sharing of sensitive content
- use Purview DLP fuction to prevent unautenticated sharing of sensitive content.
- Protect against malicious files : When you allow anonymous users to upload files, you're at an increased risk of someone uploading a malicious file. In organizations with Microsoft Defender for Office 365 Plan 1 or Plan 2 licenses (for example, in Microsoft 365 E5 or as an add-on), you can use the Safe Attachments feature to detonate uploaded files in a sandboxed virtual environment, and quarantine files that are found to be unsafe.
- Add copyright information to your files: ad a footer to a labele file.
Configure organization-level sharing settings for SharePoint and OneDrive:
Configuration Steps to share SharePoint files or folders
Go to Active sites in the new SharePoint admin center, and sign in with an account that has admin permissions for your organization.
In the left column, select a site. (For a channel site, select the link in the Channel sites column and then select the site.)
On the Settings tab, select More sharing settings.
Select an external sharing option (see the table in the next section).
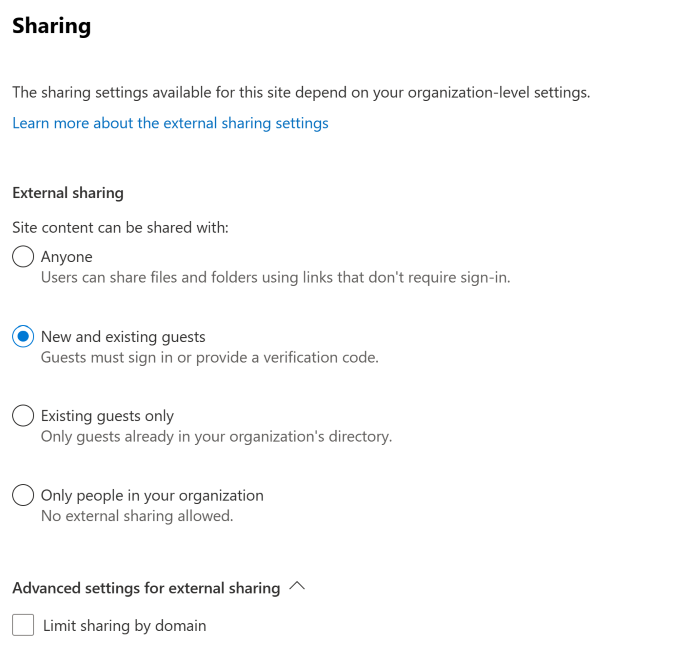
If you want to limit the sharing of this site by domain, select the Limit sharing by domain check box by expanding Advanced settings for external sharing, and add the domains that you want to allow or block.
Important
Allowed or blocked domains in Azure AD also affect SharePoint and OneDrive site sharing (always) and file and folder sharing (if Azure B2B collaboration is enabled). Be sure to review Azure AD collaboration restrictions as part of your SharePoint and OneDrive sharing setup.
If you want to change the guest access expiration setting for this site, clear the Same as organization-level setting check boxes and set the values that you want to use for this site.
If you want to change the default sharing link type or permissions for this site, clear the Same as organization-level setting check boxes and set the values that you want to use for this site. For more info, see Change the default sharing link for a site.
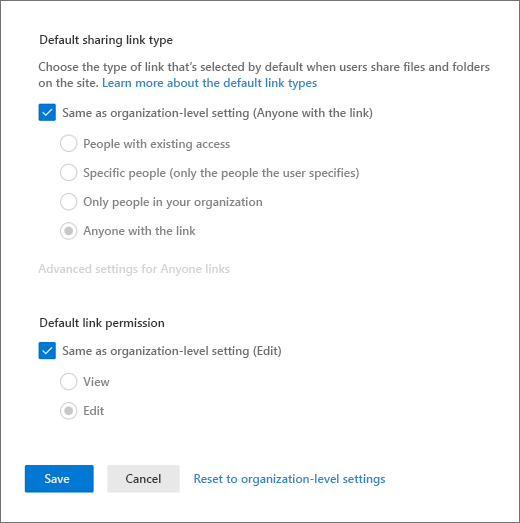
Select Save.
Configuration Steps to share OneDrive files or folders
Note
Instead of changing the external sharing setting for an individual user's OneDrive, you might want to block external sharing of sensitive information for all users. To learn how, see Learn about Microsoft Purview data loss prevention.
Sign in to https://admin.microsoft.com as a global or SharePoint admin. (If you see a message that you don't have permission to access the page, you don't have Microsoft 365 admin permissions in your organization.)
In the left pane, select Users > Active users.
Select the user.
Select the OneDrive tab, and under Sharing, select Manage external sharing.
Select a new external sharing level, and then select Save.
MS365 Group-Connected Team Site (Teams Site)
Guest Access in Microsoft Teams
Guest sharing is enabled by default in Azure AD and in Microsoft 365 (Teams, Microsoft 365 Groups, and SharePoint). This allows users to invite guests to teams and sites and to share files with them without having to request assistance from IT. You can control guest access to individual teams by using sensitivity labels.Sharing Microsoft 365 group-connected team sites
When you or your users create Microsoft 365 groups (for example in Outlook, or by creating a team in Microsoft Teams), a SharePoint team site is created. Admins and users can also create team sites in SharePoint, which creates a Microsoft 365 group. For group-connected team sites, the group owners are added as site owners, and the group members are added as site members. In most cases, you'll want to share these sites by adding people to the Microsoft 365 group. However, you can share only the site.
Most organizations will use both guest sharing and shared channels with external participants. But you must use guest sharing if:
- You want to invite people from outside your organization to the team rather than individual channels
- You want to share files or folders in a channel with people outside your organization who are not in the channel
- You want to collaborate with people outside your organization who do not have a work or school account.
Shared channels
Shared channels offer an alternative to guest access, allowing you to invite people outside your organization without requiring a guest account in Azure AD. To compare guest access with shared channels, see Plan external collaboration.
While shared channels is turned on by default in Teams, external collaboration with shared channels requires that an Azure AD administrator set up cross-tenant access between your organization and each other organization with which you want to share. Each other organization must set up cross-tenant access on their end as well.
If you plan to use shared channels with other organizations, you can choose between a self-service model and a by-request model.
- Self-service – You can configure cross-tenant access to allow inbound and outbound access to all other Azure AD organizations. Alternatively, you can block a list of organizations that you don't want your users to share with, leaving all other organizations available. This allows your users to invite people outside the organization to participate in shared channels without having to contact your helpdesk or IT department.
- By-request – You can configure cross-tenant access for each individual organization with which you want to allow shared channels. When choosing this model, it's important to have a documented business process that your users can follow to request cross-tenant access with another organization.
External participants in shared channels
External participants access shared resources in your organization by using their own Azure AD or Microsoft 365 identity. This is enabled by Azure AD B2B direct connect through an organizational relationship configured by both organizations. Guest accounts are not used in this relationship.
The primary advantage of external participants in shared channels versus guest sharing is that people outside your organization can collaborate with your users in Teams without having to change their user context. When using guest accounts, users must sign out of Teams with their work or school account and sign in again using the guest account. Alternatively, they can have a separate copy of Teams running in a private browser session. This switching between organizations takes time and can cause users to miss important communications while signed out of a given organization.
With shared channels, users can remain signed in to their organization and access channels shared with them from other organizations. Shared channels from other organizations are available in Teams alongside the teams and channels in your organization. There is no need to switch organizations.
Feature comparison
The following table describes the experiences available depending on the type of account used.
| Feature | User (your organization) | Guest (Azure AD collaboration) | External participant (Azure AD direct connect) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Team access | Y | Y | N |
| Shared channel access | Y | N | Y |
| Permissions through file sharing links | Y | Y | N |
| Use shared channels | Y | N | Y |
| Use private channels | Y | Y | N |
| Account in your directory | Y | Y | N |
| Access reviews | Y | Y | Y |
OneDrive vs SharePoint
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/sharepoint/turn-external-sharing-on-or-off
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/answers/questions/395970/what-are-the-pros-and-cons-of-using-sharepoint-onl
Same Configuration at Organization level:
- External sharing Configuration settings:
Actually, external sharing in SharePoint and OneDrive for Business has little difference, both of them can be set in organization level:
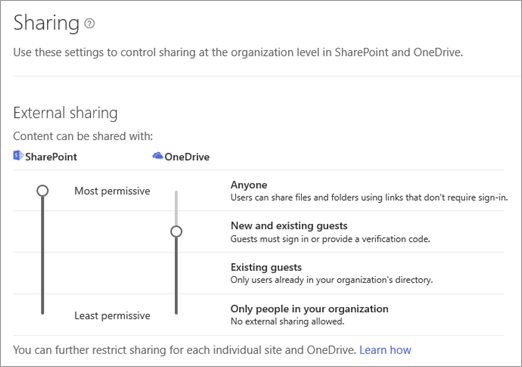
Difference configuration at site level or user level:
If files are stored in SharePoint, we can share SharePoint files or folders:
If files are stored in Personal OneDrive, we could also share OneDrive files and folders:
Other Differences:
- OneDrive is simply an online storage platform, SharePoint Online was designed as a collaboration tool for team document sharing.
- Users can access SharePoint via a branded company page that is managed by an admin, then share files in any site they have permissions, instead, users need to sign in their OneDrive for Business accouts, then share files externally.
- The SharePoint setting applies to all site types, including those connected to Microsoft 365 groups and teams.
- The OneDrive setting can be more restrictive than the SharePoint setting, but not more permissive.
More information for your reference:
https://www.sherweb.com/blog/office-365/o365-sharepoint-vs-onedrive/
----------------------------------------------Update------------------------------------------------------
Pros:
- SharePoint Online has the benefit of allowing admins to assign external sharing settings on a site by site basis, so that the ability of users to share with those outside the organization is ultimately tethered to what sites they have access to, what site the content in question is stored in, and what the settings of that individual site are.
OneDrive on the other hand takes more of an “all or nothing approach,” meaning that if one individual needs the settings on OneDrive to allow sharing with anonymous users, all other people who have access to that OneDrive environment will be able to share anonymously. In OneDrive, sharing permissions cannot be dictated on an individual level. Rather, the assigned setting will initially be “global,” and then an admin will have to go through—user by user—to disable their sharing capabilities. - External sharing in SharePoint online allows you to share documents, files, folders, lists, libraries, and complete sites,OneDrive does not support sharing sites.
- Sharing settings for OneDrive can't be more permissive than your settings for SharePoint.
Cons:
- Both SharePoint and OneDrive external sharing will increase the chances of confidential data loss when any external user can access files without logging in.
- OneDrive has same organization level sharing settings, but user level share settings are not flexible as SharePoint at site level.
OneDrive vs Teams vs SharePoint vs Blob Storage
| OneDrive | SharePoint | Teams |
| Personal | Team & Whole Company | Team |
| Private until you explicitly shared | Shared | Shared |
| One Document Library at SharePoint | Multiple Document Libraries | One Document Library, but multiple channels |
| Files in My Documents and Local | Files on File Servers | Files on File Servers |
- OneDrive : Personal Usage - My Documents - Shows everything files and folders - Store/Sharing files and folders
- Teams : For a team - Servers - small sets files / folders from SharePoint - more apps (chat, tasks, meetings, notes, polls, etc) to do all others things relating files.
- SharePoint : Whole Organization - Servers - Show sites, pages, list, documents, - Content management, Store files, collaborate and publishing over sties
References
- Microsoft Cloud Content: Why & When to Use SharePoint, OneDrive, Teams & Azure Blob Storage
- Which tool when for files: SharePoint, OneDrive, or Microsoft Teams













No comments:
Post a Comment