vCISO Academy
CISO Workshop
The workshop videos (about 4 hours total) and slides are organized into these discussions:
- Introduction and Overview of the CISO Workshop
- Part A - Key Context and Fundamentals
- Trends impacting security from the threat environment, technology, and business transformations
- Evolution of security roles and responsibilities, including key best practices and trends to monitor
- Recommended strategy and strategic initiatives to improve your program: the role of Zero Trust in strategy, the (low) cost for attackers to buy tools and passwords, learnings on getting reliable information, and a business analysis of ransomware attacks.
- Part B - Business Alignment
- Engaging business leaders on security – guidance to have a conversation in the language of leaders to explain security, key metrics to measure success of a program, and how to get support for security goals.
- Risk Insights – discusses the dual mission of security to reduce risk to the organization and enable business goals, shares tips on aligning security business goals and business risk, and shares insights on the types of attacker motivations organization’s face.
- Security Integration - guidance for successfully integrating security teams together and integrating security into IT and Business processes. Including an in-depth discussion of how to build a posture management program – an operational team focused on preventive controls (which complements the security operations (SecOps/SOC) team focused on detection, response, and recovery)
- Business Resilience – discusses how business resilience is the north star of the security program across all the security disciplines that requires balancing security investments (before, during, and after an incident) and creating a strong feedback loop. This section also includes discussion of the impact of unbalanced strategies (which is a common antipattern).
- Maturity models describing real world journeys for Risk Insights, Security Integration, and Business Resilience – including specific concrete actions to help you move up to the next level
- Part C – Security Disciplines
- Access Control - discusses how the Zero Trust approach is transforming access control, including identity and network access converging into a single coherent approach, and the emergence of the Known-Trusted-Allowed model (which updates the classic authenticated/authorized approach).
- Security Operations – discusses key leadership aspects of a security operations capability, often called SecOps or a Security Operations Center (SOC) including critical success metrics, key touchpoints with business leaders and functions, and the most important cultural elements.
- Asset Protection – discusses two key imperatives for teams that manage and secure assets (often IT Operations or Workload operations in DevOps). These teams must prioritize security work based on business criticality and must strive to efficiently scale security across the large, growing, and continuously evolving set of assets in the technical estate.
- Security Governance – discusses the role of Security Governance as a bridge between the world of business goals and technology and how this role is changing with the advent of cloud, digital and zero trust transformations. This section also covers key components of security governance including risk, compliance, security architecture, posture management, (strategic) threat intelligence, and more.
- Innovation Security - discussion of how application security evolves into a modern approach (including DevSecOps) and key focus areas to drive success of this capability.
- Security Governance Maturity models describing real world journeys for Security Architecture, Posture Management, and IT Security Maintenance – including specific concrete actions to help you move up to the next level
- Next Steps/Closing – wraps up the workshop with key quick wins and next steps
Imperative: Coverage for commom attack chains (Insider and external threats)
Microsoft Digital Defense Report:
https://aka.ms/MDDR = https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/security/business/microsoft-digital-defense-report-2022
Mindmap
- Cyber Security Mind Map Examples:
- 网络安全绪论
- 扫描与防御技术
- 口令破解及防御技术
- 拒绝服务供给与防御技术
- Web及防御技术
- 计算机病毒
- 网络安全发展与未来
- 企业安全工作要点思维导图
- Free Cloud Mind Map Website: Mind Mup2 - https://drive.mindmup.com/
 |
| SANS Cisco Mind Map |
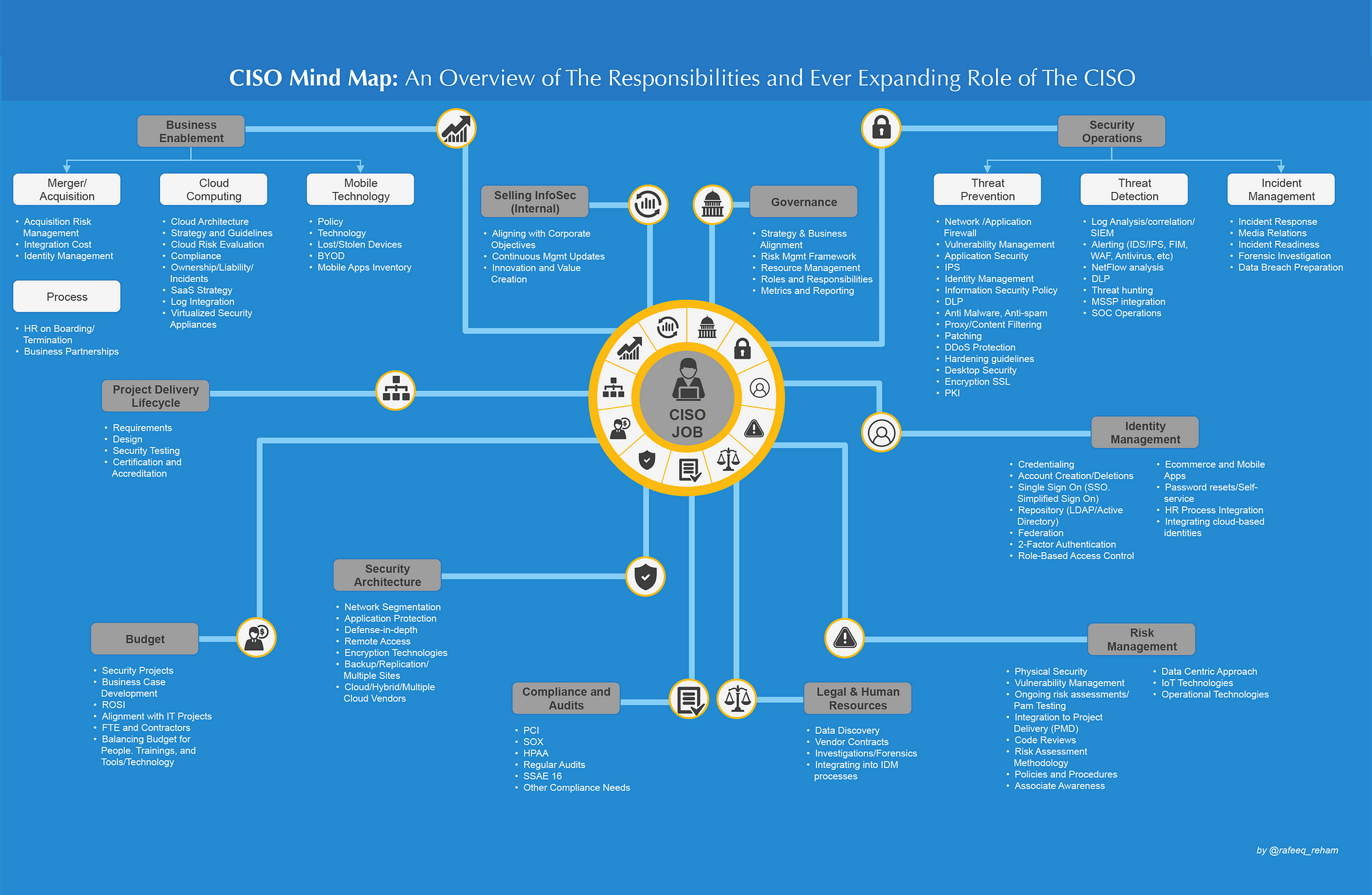
A CISO (Chief Information Security Officer) has a complex role within a company. They have a wide array of tasks to perform, that involves many differing parts, which the average individual is not always aware of.
CISO Mind Map is an overview of responsibilities and ever expanding role of the CISO. This Security Leadership poster made by SANS shows exactly the matters a CISO needs to mind when creating a world class IT Security team. It also highlights the essential features necessary of a Security Operations Centre (SOC).
To make this chart more practical, I put them into the tables and will update it with some technologies and thoughts applied in my daily work. This update will last a long term. It will be put into navigation bar for easy access.
Security Operations
Prevention
|
Detection
|
Response
|
|
|
|
Legal and Regulatory
| Compliance | Privacy | Audit | Investigation |
|
|
|
|
| Intellectual Property | Contract Review | Customer Requirments | Lawsuit Risk & Acts |
|
|
|
|
Risk Management
| Risk Framework | Risk Assessment Methodology | Business Impact Analysis |
|
|
|
| Risk Assessment Process | Risk Analysis and Quantification | Security Awareness |
|
||
| Vulnerability Management | Vendor Risk Management | Physical Security |
|
|
|
| Disaster Recovery (DR) | Business Continuity Planning | Risk Treatment |
|
||
| Policies and Procedures | ||
| ||
Business Enablement
| Product Security | Cloud Computing | Mobile |
|
|
|
| Emerging Technologies | Mergers and Acquisitions | |
|
|
Governance
| Strategy | Business Alignment | Risk Management |
| ||
| Program Frameworks | Control Frameworks | Program Structure |
|
| |
| Program Management | Communications Plan | Roles and Responsibilities |
| Workforce Planning | Resource Managemnet | Data Classification |
| ||
| Security Policy | Create a Security Culture | Security Training |
|
| |
| Metrics and Reporting | IT Portfolio Management | Change Management |
|
| |
| Board Communications | ||
|
Identify and Access Management
Provisioning/
Deprovisioning
|
Single Sign On
(SSO)
|
Federated Single Sing on (FSSO)
|
Multi-Factor Authentication
|
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
| Identity Store (LDAP, ActiveDirectory) |
Leadership Skills
| Business Strategy | Industry Knowledge | Business Acumen |
| Communication Skills | Presentation Skills | Strategic Planning |
| Technical Leadership | Security Consulting | Stakeholder Management |
|
| |
| Negotiations | Mission and Vision | Values and Culture |
| Roadmap Development | Business Case Development | Project Management |
|
| |
| Employee Development | Financial Planning | Budgeting |
| Innovation | Marketing | Leading Change |
| Customer Relationships | Team Building | Mentoring |
|
Note: ISO = Information Security Office
Another CISO Mind Map example:
Note: The original image concept was created by Rafeeq Rehman and later redesigned by Momentum Partners.
CISO Job and Priority
CISO’s Guide to Cost-Effective Priorities
Compliance:
- Develop the list of interested parties related to information security (see also How to identify interested parties according to ISO 27001 and ISO 22301)
- Develop the list of requirements from interested parties
- Remain in continuous contact with authorities and special interest groups
- Coordinate all efforts related to personal data protection
Documentation:
- Propose the draft of main information security documents – e.g., Information security policy, Classification policy, Access control policy, Acceptable use of assets, Risk assessment and risk treatment methodology, Statement of Applicability, Risk treatment plan, etc.
- Be responsible for reviewing and updating main documents
- Risk management:
- Teach employees how to perform risk assessment
- Coordinate the whole process of risk assessment (see also: ISO 27001 risk assessment & treatment – 6 basic steps)
- Propose the selection of safeguards
- Propose the deadlines for safeguards implementation
- Perform background verification checks of job candidates
- Prepare the training and awareness plan for information security (see also How to perform training & awareness for ISO 27001 and ISO 22301)
- Perform continuous activities related to awareness raising
- Performing induction training on security topics for new employees
- Propose disciplinary actions against employees who performed the security breach
- Communicate the benefits of information security (see also Four key benefits of ISO 27001 implementation)
- Propose information security objectives (see also ISO 27001 control objectives – Why are they important?)
- Report on the results of measuring
- Propose security improvements and corrective actions
- Propose budget and other required resources for protecting the information
- Report important requirements of interested parties
- Notify top management about the main risks
- Report about the implementation of safeguards
- Advise top executives on all security matters
- Ensure that all corrective actions are performed
- Verify if the corrective actions have eliminated the cause of nonconformities
- Maintain an inventory of all important information assets
- Delete the records that are not needed any more
- Dispose of media and equipment no longer in use, in a secure way
- Perform risk assessment for activities to be outsourced
- Perform background check for candidates for outsourcing partners
- Define security clauses that must be part of an agreement
- Define which type of communication channels are acceptable and which are not
- Prepare communication equipment to be used in case of an emergency / disaster
- Receive information about security incidents
- Coordinate response to security incidents
- Prepare evidence for legal action following an incident
- Analyze incidents in order to prevent their recurrence
- Coordinate the business impact analysis process and the creation of response plans
- Coordinate exercising and testing
- Perform post-incident review of the recovery plans
- Approve appropriate methods for the protection of mobile devices, computer networks and other communication channels
- Propose authentication methods, password policy, encryption methods, etc.
- Propose rules for secure teleworking
- Define required security features of Internet services
- Define principles for secure development of information systems
- Review logs of user activities in order to recognize suspicious behavior
How to start your first 100 days as CISO
Goals:
- Establish, Oversee and Manage Organizational Security
- Foster Trust with Security Goals
- Make Security a Business Enabler
Pitfalls to Avoid
- Putting out fires
- Getting caught up in organizational politics
- Using manual processes instead of automation
- Forgetting about compliance
- Doing everything yourself
- Forgetting to set expectations with the client
- Being too dogmatic
- Avoiding challenging paradigms and decisions
- Juggling too many industries
- Forgetting to integrate data from other parts of the business
The 5 Phases: Your 100 Day Action Plan
- Research (Days 0-30): Meeting stakeholders and management, meeting the IT/security team, reviewing past security incidents and responses
- Meet stakeholders and management to understand their expectations and learn about the organization.
- Meet the IT/security team to build relationships, evaluate the team's skills, understand current workflows, and identify any gaps in expertise or resources.
- Get access to tools, data and all relevant systems so you can review configurations, management practices, and security controls.
- Analyze existing infrastructure, tools, frameworks, policies and reports to gain insights into potential vulnerabilities and the effectiveness of existing security controls and procedures.
- Obtain and understand network and data flow diagrams to recognize critical data flows and potential points of exposure.
- Review past security incidents and responses to evaluate the organization’s ability to respond and recover from such incidents.
- Conduct threat intelligence research of the threat landscape, including CVEs, zero-days, regulations and key players. Take note of which threat actors are targeting these types of clients, how they get access, and preferred methods of persistence.
- Understand the existing vendor management process to reveal third-party risks and compliance with security policies.
- Review customer contracts to ensure that customer-imposed security requirements are met, as these can influence the prioritization of security tasks.
- Understand the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) program to see how security is integrated into application development (when applicable).
- Understand (Days 0-45): Conducting a security risk assessment, showing the current security posture and gaps to the management, identifying short-term and long-term needs
- Conduct a security risk assessment. Taking all the info you've gathered, you'll want to begin to collate and synthesize it in a formal risk assessment to baseline the environment.
- Use a standard onboarding questionnaire and scanning tool to provide objective assessment of current risks.
- Create a clear picture of security maturity and the security posture. Compile the data from your initial assessments into clear, executive-friendly reports that include technical metrics and an evaluation of the processes, people, and technology in place. Use established cybersecurity frameworks like NIST to measure the organization's security practices against industry benchmarks.
- Show the current security posture and gaps to the management. Present a gap analysis to management that clearly delineates where the organization stands versus where it needs to be. This should be done in the context of the organization's risk appetite, regulatory requirements and business goals.
- Identify short-term and long-term needs. Based on the gap analysis, develop a prioritized list of risks and associated remediation steps that align with business objectives, distinguishing between immediate (short-term) and strategic (long-term) needs.
- Identify business needs. Perform an analysis of how security investments translate into business value, considering factors like reduced downtime, compliance fines avoided, and reputational benefits.
- Examine the use of automation. Identify areas where security processes can be automated for efficiency, like risk and compliance assessments, gap analysis, tailored policies, creation of strategic remediation plans with prioritized tasks, use of tools for ongoing task management, progress tracking and customer-facing reports
- Prioritize (Days 15-60): Defining short, mid and long-term goals, creating a remediation/work plan based on those goals, planning budgets and resources
- Define short, mid and long-term goals. Draft specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for the current 100 days, the end of the year, and the following year. These goals should focus on mitigating
- the most significant risks first.
- Create a remediation/work plan based on those goals that lays out the steps necessary to achieve each goal. This should include timelines, responsible parties and expected outcomes.
- Identify 2-3 quick wins that can improve security posture with minimal effort or investment. For example, enabling MFA or optimizing existing security tool configurations for better coverage.
- Plan budgets and resources for security initiatives, ensuring cost-effectiveness and alignment with broader financial planning. Assess where automation can reduce the need for additional resources and streamline existing operations, to save costs and improve efficiency.
- Create a risk register that documents all identified risks along with their likelihood and impact and prioritizes them.
- Share the goals and high level plan with the management, ensuring transparency and setting the stage for ongoing support and engagement from the top down.
- Execute (Days 30-80): Communicating the plan to all stakeholders, implementing automated systems that can deliver low hanging fruit, setting a cadence for external scanning and reporting
- Get stakeholder and management buy-in by explaining the strategic plan, its benefits, and its impact on the organization. Ensure that the value of your proposed security measures is clearly understood.
- Communicate the plan to all stakeholders - vertical and horizontal. Ensure that all departments feel included and responsible for its success.
- Implement automated systems that can deliver low hanging fruit. Here are some examples, but the right automated system will depend on the vertical and company type.
- Automated password reset platforms
- Automated report generation
- Accounting systems that require dual approval for money transfers
- A vCISO platform
- Orchestration platforms that can automate cog deployments to prevent misconfigurations
- RPA (Robotic Process Automation) providers for enforcing JIT (Just in Time) admin access
- Automated code scanning or static testing tools
- Focus on the quick, impactful wins that you identified, like policy updates or turning on unused but available security features. This helps build momentum and demonstrates early successes.
- Start with high priority policy creation, such as those governing incident response, data protection, and access control.
- Recommend purchasing products or tools if needed.
- Set a cadence for external scanning and reporting, demonstrating improvement and risk reduction over time.
- Continuously manage and adjust remediation plans to ensure they remain effective and responsive.
- Report (Days 45-100): Measuring success, communicating progress at least once a month, integrating reporting into your overall plan
- Measure Success by collecting and analyzing data that reflects the success of the executed plan. This could include metrics such as:
- Reduced incident response times
- Fewer successful phishing attempts
- Improvement in security and compliance postures
- Reduced risk levels for malicious activities like data leaks, ransomware, fraud and website defacement
- Higher scores for domains like access management, threat intelligence, passwords, website and data protection
- Advancement in task progress
- Craft detailed reports for management that articulate successes, challenges, and areas requiring attention. Reports should translate technical operations into business impacts, making it easy for executives to understand the return on their security investments.
- Communicate progress at least once a month, ensuring transparency and maintaining the urgency of cybersecurity initiatives. Pro tip: Use the same standard reports to make reporting easier to create and to consume.
- Integrate reporting into your overall plan, reflecting on how the security measures contribute to the overall business strategy and risk management framework.
- Conduct an additional full assessment after 3-4 months to demonstrate progress and identify any new or unresolved vulnerabilities.
- Reassess and Reajust:
- Use the findings from continuous assessments to realign the security strategy with the
- organization's evolving needs and threat landscape.
- Prioritize new initiatives or scale back on those that are less effective.
- Work closely with the executive team to interpret report findings and plan for the coming
- quarters.
- Continuously adapt and improve your processes and controls to keep security measures
- effective and relevant.
Sample Questions to Ask Stakeholders
- Can you list the mission-critical applications your department uses daily?
- What data types are most commonly processed within these applications?
- Could you walk me through the business workflow using these systems?
- What types of payment methods are processed, and through what systems?
- What are your primary concerns about your current systems and data security?
- What ongoing projects are being conducted?
- What are your specific expectations from the vCISO service and this engagement?
CISA Tabletop Exercise Packages
CISA Tabletop Exercise Packages (CTEPs) are a comprehensive set of resources designed to assist stakeholders in conducting their own exercises. Partners can use CTEPs to initiate discussions within their organizations about their ability to address a variety of threat scenarios.
Each package is customizable and includes template exercise objectives, scenarios, and discussion questions as well as a collection of references and resources. Available scenarios cover a broad array of physical security and cybersecurity topics, such as natural disasters, pandemics, civil disturbances, industrial control systems, election security, ransomware, vehicle ramming, insider threats, active assailants, and unmanned aerial systems. CTEPs also provide scenario and module questions to discuss pre-incident information and intelligence sharing, incident response, and post-incident recovery.
With over 100 CTEPs available, stakeholders can easily find resources to meet their specific exercise needs.
Cybersecurity Scenarios
These CTEPs include cybersecurity-based scenarios that incorporate various cyber threat vectors including ransomware, insider threats, phishing, and Industrial Control System (ICS) compromise. There are also sector-specific cybersecurity scenarios for elections infrastructure, local governments, maritime ports, water, and healthcare.
Physical Security Scenarios
Active shooters, vehicle ramming, improvised explosive devices (IEDs), unmanned aircraft systems (UASs), and many more. There are also CTEPs that are geared towards specific industries or facilities to allow for discussion of their unique needs.
Cyber-Physical Convergence Scenarios
Physical impacts resulting from a cyber threat vector, or cyber impacts resulting from a physical threat vector. While CTEPs within the cyber and physical sections may touch on these subjects, convergence CTEPs are designed to further explore the impacts of convergence and how to enhance one’s resiliency.
CTEP Documents
Leverage pre-built templates to develop a full understanding of roles and responsibilities for exercise planners, facilitators / evaluators, and participants. Additionally, the documentation includes templates for the initial invitation to participants, a slide deck to use for both planning meetings and conduct, a feedback form to distribute to participants post-exercise, and an After Action Report. In conjunction with selecting one of the above situation manuals, your exercise planning team will be able to fully develop your own tabletop exercise and update information sharing processes; emergency response protocols; and recovery plans, policies, and procedures.













No comments:
Post a Comment