 A Threat and Risk Assessment analyzes a software or hardware system for vulnerabilities, examines potential threats associated with those vulnerabilities, and evaluates the resulting security risks. A vulnerability is any “flaw or weakness in system security procedures, design, implementation, or internal controls that could be exercised (accidentally triggered or intentionally exploited) and result in a security breach or a violation of the system's security policy” (NIST SP800-30 Risk Management Guide for Information Technology Systems). The level of threat is determined from the potential for any natural, human or environmental source to trigger or exploit any identified vulnerability. The risk assessment looks at both the probability of that threat occurring, and the impact on both system and organization should it occur. An appropriate strategy can then be formulated for each risk depending on severity (such as acceptance of the risk, adoption of a mitigation plan, or implementation of an avoidance strategy).
A Threat and Risk Assessment analyzes a software or hardware system for vulnerabilities, examines potential threats associated with those vulnerabilities, and evaluates the resulting security risks. A vulnerability is any “flaw or weakness in system security procedures, design, implementation, or internal controls that could be exercised (accidentally triggered or intentionally exploited) and result in a security breach or a violation of the system's security policy” (NIST SP800-30 Risk Management Guide for Information Technology Systems). The level of threat is determined from the potential for any natural, human or environmental source to trigger or exploit any identified vulnerability. The risk assessment looks at both the probability of that threat occurring, and the impact on both system and organization should it occur. An appropriate strategy can then be formulated for each risk depending on severity (such as acceptance of the risk, adoption of a mitigation plan, or implementation of an avoidance strategy).Define TRA Methodology
NIST SP 800-30 Rev. 1 - Guide for Conducting Risk Assessments
FIPS 200 - Minimum Security Requirements for Federal Information and Information Systems
FIPS 199 - Standards for Security Categorization of Federal Information and Information Systems
Define Process
Based on FIPS 200, the generalized format for expressing the security category (SC) of an information system is:
SC information system = {(confidentiality, impact), (integrity, impact), (availability, impact)},
where the acceptable values for potential impact are low, moderate, or high.
Since the potential impact values for confidentiality, integrity, and availability may not always be the same for a particular information system, the high water mark concept must be used to determine the overall impact level of the information system.
Define Scope
Organizations must meet the minimum security requirements in this standard by selecting the appropriate security controls and assurance requirements as described in NIST Special Publication 800-53, Recommended Security Controls for Federal Information Systems
The selected set of security controls must include one of three, appropriately tailored8 security control baselines from NIST Special Publication 800-53 that are associated with the designated impact levels of the organizational information systems as determined during the security categorization process. - For low-impact information systems, organizations must, as a minimum, employ appropriately tailored security controls from the low baseline of security controls defined in NIST Special Publication 800-53 and must ensure that the minimum assurance requirements associated with the low baseline are satisfied. - For moderate-impact information systems, organizations must, as a minimum, employ appropriately tailored security controls from the moderate baseline of security controls defined in NIST Special Publication 800-53 and must ensure that the minimum assurance requirements associated with the moderate baseline are satisfied. - For high-impact information systems, organizations must, as a minimum, employ appropriately tailored security controls from the high baseline of security controls defined in NIST Special Publication 800-53 and must ensure that the minimum assurance requirements associated with the high baseline are satisfied.
Example One - Quantitative TRA
Step #1: Identify and Prioritize Assets
Step #2: Identify Threats
Step #3: Identify Vulnerabilities
Step #4: Analyze Controls
Step #5: Determine the Likelihood of an Incident
Step #6: Assess the Impact a Threat Could Have
Step #7: Prioritize the Information Security Risks
Step #8: Recommend Controls
Step #9: Document the Results
A useful tool for estimating risk in this manner is the risk-level matrix. A high likelihood that the threat will occur is given a value of 1.0; a medium likelihood is assigned a value of 0.5; and a low likelihood of occurrence is given a rating of 0.1. Similarly, a high impact level is assigned a value of 100, a medium impact level 50, and a low impact level 10. Risk is calculated by multiplying the threat likelihood value by the impact value, and the risks are categorized as high, medium or low based on the result.
For example:
For Malicious human - DDOS attack with Firewall vulnerability on Website asset:
Threat = high =100 (1,50,100,120)
Vulnerability = low = 0.1 (0.1,0.5,1)
Asset = Critical = 10 (1,5,10)
Impact = Critical =Threat x Vulnerability x Asset Value = 100*0.1*10=100
Likelihood = Medium = 0.5 (0.1,0.5,1)
Risk = Impact x Likelihood = 100 x 0.5 = 50 --> Medium
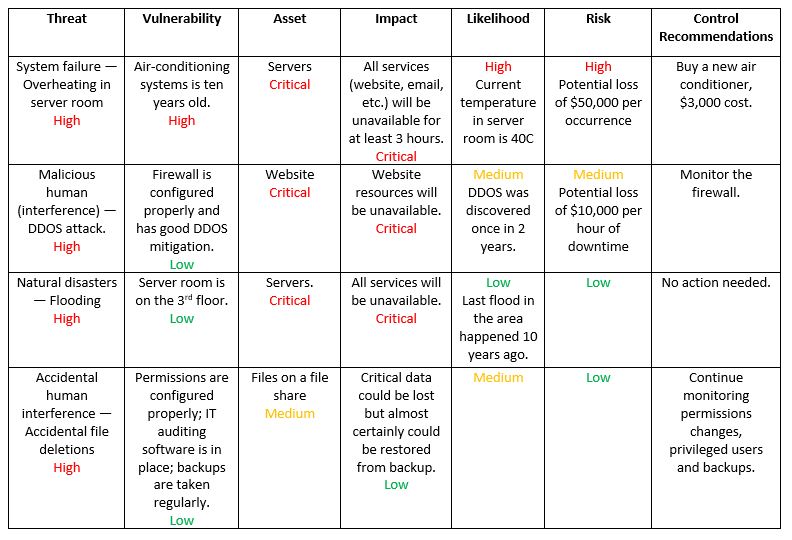
Reference: https://blog.netwrix.com/2018/01/16/how-to-perform-it-risk-assessment/
For example:
For Malicious human - DDOS attack with Firewall vulnerability on Website asset:
Threat = high =100 (1,50,100,120)
Vulnerability = low = 0.1 (0.1,0.5,1)
Asset = Critical = 10 (1,5,10)
Impact = Critical =Threat x Vulnerability x Asset Value = 100*0.1*10=100
Likelihood = Medium = 0.5 (0.1,0.5,1)
Risk = Impact x Likelihood = 100 x 0.5 = 50 --> Medium

Example Two : Qualitative TRA
| Category | Security Control | Low | Moderate | High |
| Access Control | Administrator Multi Factor Authentication | x | x | |
| Access Control | Centralized Authentication | x | x | |
| Access Control | Machine Authentication | x | x | |
| Access Control | Physical Security | x | x | x |
| Access Control | Role-based Authentication / Least Privilege | x | x | |
| Access Control | Separation of duties | x | x | |
| Access Control | User Multi Factor Authentication | x | ||
| Audit | Audit Data Review | x | x | x |
| Audit | Login Audit | x | x | x |
| Configuration Management | Configuration Change Control | x | x | x |
| Configuration Management | Notification of changes | x | ||
| Configuration Management | System Component Inventory | x | x | x |
| Contingency Planning | Contingency Plan | x | x | x |
| Contingency Planning | Disaster Recovery Site | x | ||
| Contingency Planning | Offsite Backup | x | x | |
| Contingency Planning | Onsite Backup | x | x | x |
| Incident Response | Incident Response | x | x | x |
| Media Protection | Secure Delete | x | x | |
| Risk Assessment | Penetration Testing | x | ||
| Risk Assessment | Vulnerability Management | x | x | x |
| System and Communication Protection | Data Leak Protection (DLP) | x | x | |
| System and Communication Protection | DoS Protection | x | ||
| System and Communication Protection | Encryption at rest | x | x | |
| System and Communication Protection | Encryption in transit | x | x | x |
| System and Communication Protection | Isolation in multi-tenant environment | x | x | |
| System and Communication Protection | Network Segregation | x | ||
| System and Information Integrity | Antivirus/Antimalware | x | x | x |
| System and Information Integrity | File Integrity Monitoring | x | x | |
| System and Information Integrity | Host IDS | x | ||
| System and Information Integrity | Network IDS | x | x | |
| System and Information Integrity | Patch Management | x | x | x |
| System and Information Integrity | Priviledged Access Management | x | ||
| System and Information Integrity | System Hardening | x | x | x |
| System and Information Integrity | System Health Monitoring | x | x | x |
| Training | Awareness and Training | x | x | x |
A Step-by-Step Guide to Cybersecurity TRA
1. Understanding Cybersecurity Risk Assessment
In today's digital age, cybersecurity has become a critical concern for individuals and businesses alike. Cybersecurity risk assessment is the process of identifying, evaluating, and managing potential cyber threats to your digital assets. It involves assessing the likelihood and impact of various cyber risks and developing strategies to mitigate them.
Cybersecurity risk assessment is an essential component of any comprehensive cybersecurity program. It helps you identify vulnerabilities in your systems and processes that could be exploited by cybercriminals. By understanding the risks, you can develop effective strategies to protect your digital assets and minimize the impact of any potential attacks.
The first step in cybersecurity risk assessment is to understand the nature of the threat landscape. This includes identifying the types of cyber threats that are most likely to affect your organization, such as malware, phishing attacks, or ransomware. You should also consider the potential sources of these threats, including external attackers, insider threats, and third-party vendors.
Once you have identified the potential threats, you need to evaluate the vulnerabilities in your systems and processes that could be exploited by cybercriminals. This includes assessing the security of your networks, applications, and data storage systems. You should also consider the effectiveness of your security controls, such as firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems.
Finally, you need to develop a comprehensive risk management plan that outlines the steps you will take to mitigate the identified risks. This may include implementing additional security controls, training employees on cybersecurity best practices, and establishing incident response procedures.
Overall, cybersecurity risk assessment is a critical process for protecting your digital assets from cyber threats. By understanding the nature of the risks and developing effective strategies to mitigate them, you can ensure the security and integrity of your systems and data.
2. Identifying Potential Cyber Threats
In order to effectively secure your digital assets, it's important to identify potential cyber threats. These threats can come in many forms, including malware, phishing attacks, hacking attempts, and more. It's important to understand that these threats are constantly evolving, so it's crucial to stay up-to-date on the latest trends and tactics used by cybercriminals.
One way to identify potential cyber threats is to conduct a thorough analysis of your organization's systems and networks. This can include reviewing logs and monitoring activity for any suspicious behavior. Additionally, it's important to stay informed about any new vulnerabilities or exploits that may be discovered in commonly used software or hardware.
Another key aspect of identifying potential cyber threats is to stay aware of social engineering tactics. These can include phishing emails, phone calls, or other attempts to trick employees into divulging sensitive information or granting access to unauthorized individuals. By educating employees about these tactics and implementing strong security protocols, you can help prevent these types of attacks from being successful.
Overall, identifying potential cyber threats requires a combination of vigilance, awareness, and ongoing education. By staying informed and proactive, you can help protect your digital assets from a wide range of cyber threats.
3. Evaluating Vulnerabilities and Impact
Evaluating vulnerabilities and impact is a crucial step in cybersecurity risk assessment. It involves identifying weaknesses in your digital assets that could be exploited by cybercriminals and assessing the potential impact of a successful attack.
To evaluate vulnerabilities, you need to conduct a thorough analysis of your systems, networks, and applications. This includes identifying any outdated software or hardware, unsecured access points, weak passwords, and other security gaps that could be exploited.
Once you have identified vulnerabilities, you need to assess their potential impact on your organization. This involves considering factors such as the type of data that could be compromised, the financial cost of a breach, and the reputational damage that could result.
By evaluating vulnerabilities and impact, you can prioritize your cybersecurity efforts and develop a plan to address the most critical risks first. This will help you to minimize the likelihood of a successful cyber attack and reduce the potential impact if one does occur.
4. Developing a Comprehensive Risk Management Plan
After identifying potential cyber threats and evaluating vulnerabilities and impact, the next step is to develop a comprehensive risk management plan. This plan should outline specific actions that will be taken to mitigate risks and protect digital assets.
One important aspect of a risk management plan is establishing clear protocols for responding to security incidents. This includes defining roles and responsibilities for key personnel, as well as outlining procedures for reporting and investigating incidents.
Another critical component of a risk management plan is implementing appropriate security measures. This may include installing firewalls and antivirus software, using strong passwords and encryption, and regularly backing up data.
It's also essential to establish ongoing monitoring and testing procedures to ensure that security measures are effective and up-to-date. Regularly reviewing and updating the risk management plan is also crucial, as new threats and vulnerabilities can emerge over time.
Overall, developing a comprehensive risk management plan requires careful consideration of potential threats and vulnerabilities, as well as a commitment to ongoing monitoring and improvement. By taking these steps, individuals and organizations can better protect their digital assets and reduce the risk of cybersecurity incidents.








No comments:
Post a Comment