SSL/TLS use of weak RC4(Arcfour) cipher port 3389/tcp over SSL
 QID: 38601
QID: 38601Category: General remote services
CVE ID: CVE-2013-2566, CVE-2015-2808
Vendor Reference: -
Bugtraq ID: 91787, 58796, 73684
Service Modified: 05/10/2019
User Modified: -
Edited: No
PCI Vuln: Yes
THREAT:
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL v2/v3) and Transport Layer Security (TLS ) protocols provide integrity, confidentiality and authenticity services to other
protocols that lack these features.
SSL/TLS protocols use ciphers such as AES,DES, 3DES and RC4(Arcfour) to encrypt the content of the higher layer protocols and thus provide the
confidentiality service. Normally the output of an encryption process is a sequence of random looking bytes. It was known that RC4 output has some
bias in the output. Recently a group of researchers has discovered that the there is a stronger bias in RC4(Arcfour) , which make statistical analysis
of ciphertext more practical.
The described attack is to inject a malicious javascript into the victim's browser that would ensure that there are multiple connections being
established with a target website and the same HTTP cookie is sent multiple times to the website in encrypted form. This provides the attacker a
large set of ciphertext samples, that can be used for statistical analysis.
NOTE: On 3/12/15 NVD changed the CVSS v2 access complicity from high to medium. As a result Qualys revised the CVSS score to 4.3
immediately. On 5/4/15 Qualys is also revising the severity to level 3.
IMPACT:
If this attack is carried out and an HTTP cookie is recovered, then the attacker can use the cookie to impersonate the user whose cookie was
recovered.
This attack is not very practical as it requires the attacker to have access to millions of samples of ciphertext, but there are certain assumptions that
an attacker can make to improve the chances of recovering the cleartext from cihpertext. For examples HTTP cookies are either base64 encoded or
hex digits. This information can help the attacker in their efforts to recover the cookie.
SOLUTION:
RC4 should not be used where possible. One reason that RC4(Arcfour) was still being used was BEAST and Lucky13 attacks against CBC mode
ciphers
in SSL and TLS. However, TLSv 1.2 or later address these issues.
COMPLIANCE:
Not Applicable
EXPLOITABILITY:
There is no exploitability information for this vulnerability.
ASSOCIATED MALWARE:
There is no malware information for this vulnerability.
RESULTS:
CIPHER KEY-EXCHANGE AUTHENTICATION MAC ENCRYPTION(KEY-STRENGTH) GRADE
TLSv1 WITH RC4 CIPHERS IS SUPPORTED
RC4-MD5 RSA RSA MD5 RC4(128) MEDIUM
RC4-SHA RSA RSA SHA1 RC4(128) MEDIUM
TLSv1.1 WITH RC4 CIPHERS IS SUPPORTED
RC4-MD5 RSA RSA MD5 RC4(128) MEDIUM
RC4-SHA RSA RSA SHA1 RC4(128) MEDIUM
TLSv1.2 WITH RC4 CIPHERS IS SUPPORTED
RC4-MD5 RSA RSA MD5 RC4(128) MEDIUM
RC4-SHA RSA RSA SHA1 RC4(128) MEDIUM
Fix
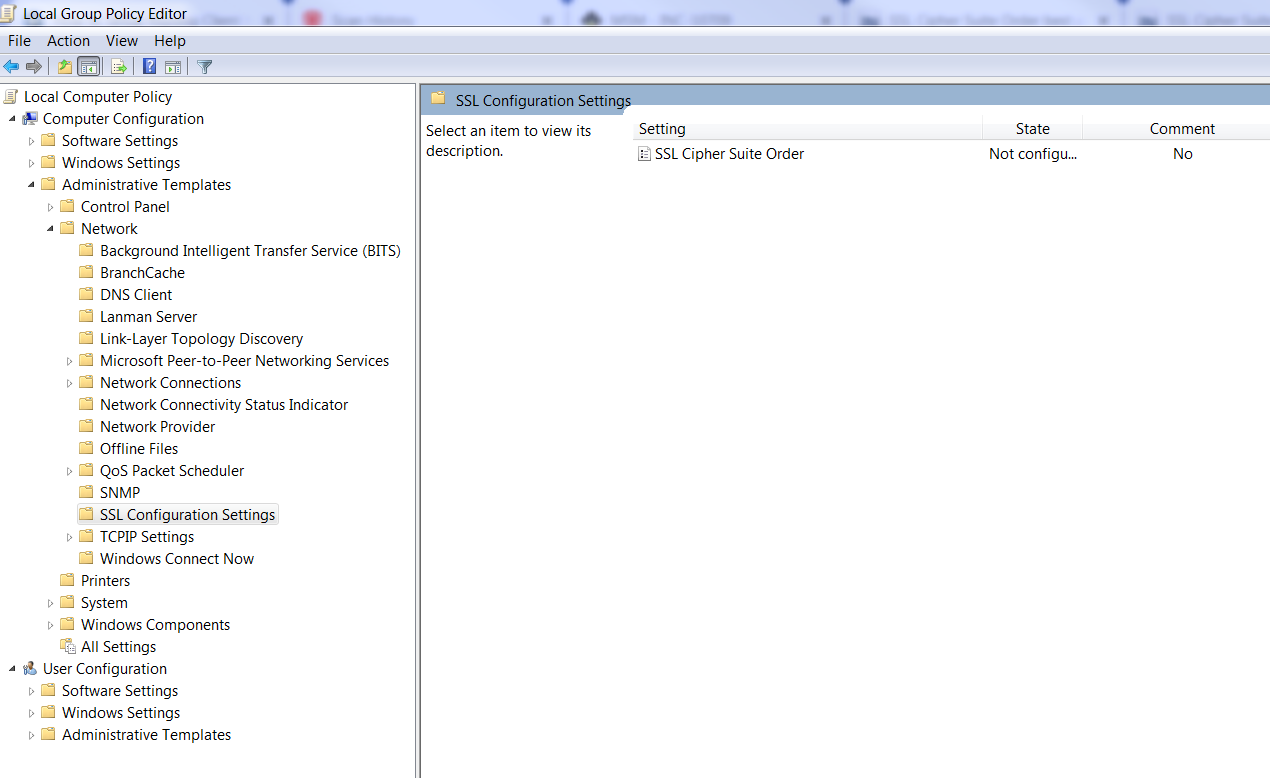
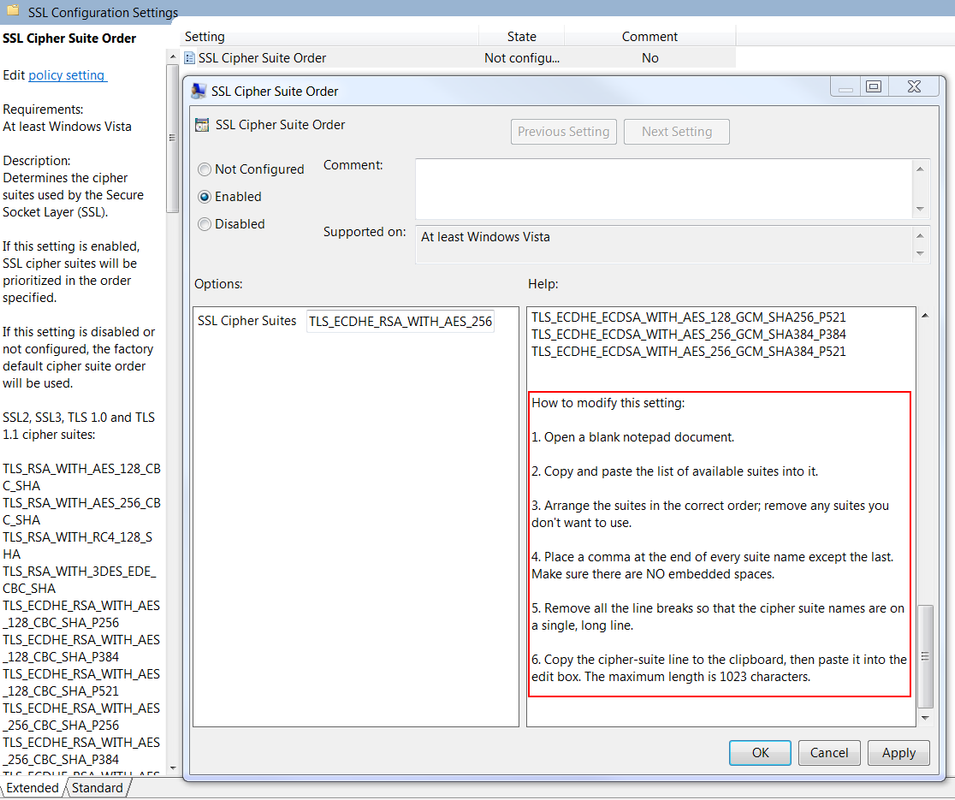
Basically, we will need to change SSL Cipher Suite Order settings to remove RC4 from the list. The way to change the cipher suite order is to use Group Policy > Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Network > SSL Configuration Settings > SSL Cipher Suite Order.Run GPEDIT from adminsitrator account.
Also from Microsoft security advisory: update for disabling RC4.
Clients and servers that do not want to use RC4 regardless of the other party’s supported ciphers can disable RC4 cipher suites completely by setting the following registry keys. In this manner, any server or client that is talking to a client or server that must use RC4 can prevent a connection from occurring. Clients that deploy this setting will be unable to connect to sites that require RC4, and servers that deploy this setting will be unable to service clients that must use RC4.
- [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Ciphers\RC4 128/128]
"Enabled"=dword:00000000 - [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Ciphers\RC4 40/128]
"Enabled"=dword:00000000 - [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Ciphers\RC4 56/128]
"Enabled"=dword:00000000







No comments:
Post a Comment