What is discovery in Thycotic Secret Server:
- Discovery finds secrets in an IT environment and imports them into secret server.
- Secret server is most effective when it covers all privileged accounts
- Discovery helps to eliminate,
- Unknown privileged accounts
- Backdoor Access
- Gaps in security
- Auditors want automated processes to reduce human mistakes
Discovery types
Out-of-box:
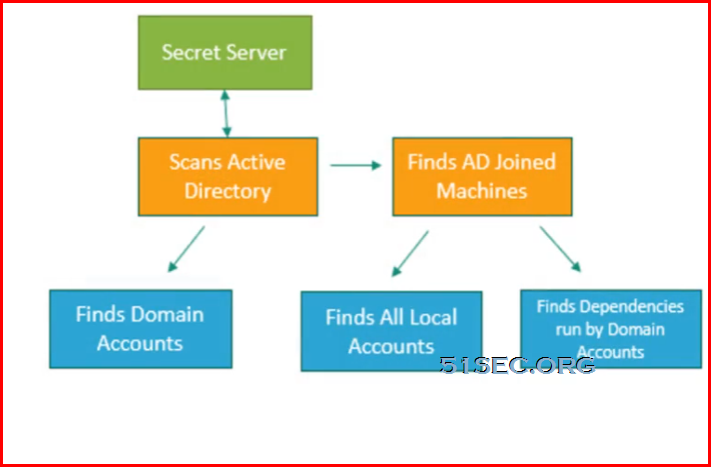
- AD (using LDAPs and WMI)
- Domain Computers' local accounts
- Domain accounts
- Domain accounts running
- Window Services
- Scheduled Tasks
- IIS Application Pools
- IIS Application Pool Recycles
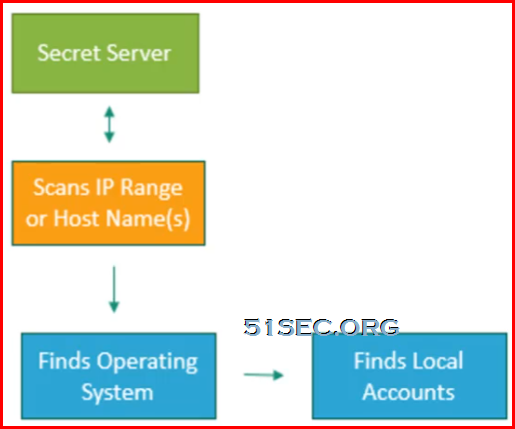
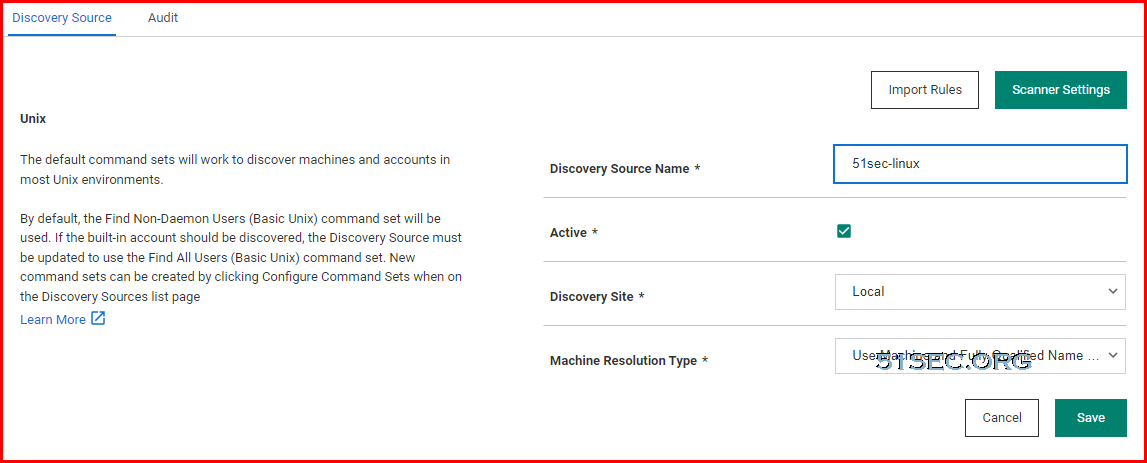
- Unix/Linux Local accounts
- Machines - finds out Operating System first then local accounts
- Non-Daemon Users - most other user accounts
- All users - built-in accounts
- Scanning accounts
- need to be able to connect over ssh
- read /etc/passwd
- minimum permissions for taking over account during import sudoer permissions
- sudoer permissions on /etc/passwd
- Define host range
- IP address
- Host name
- IP address range
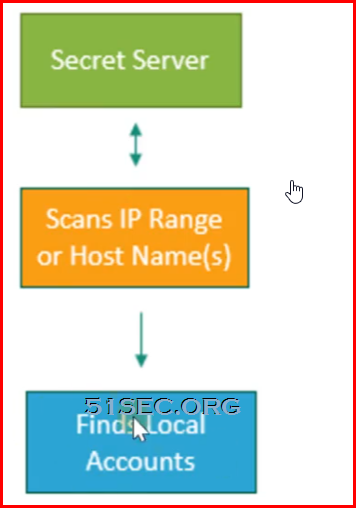
- Hypervisor ESXi accounts
- vSphere PowerCLI 5.5 release 2 - API installed on your Secret server
- PowerShell 3 or greater on your secret server
- Scanning accounts
- Shell Access
- Query VRM policy permission
- Define host range
- IP address
- Host name
- IP address range
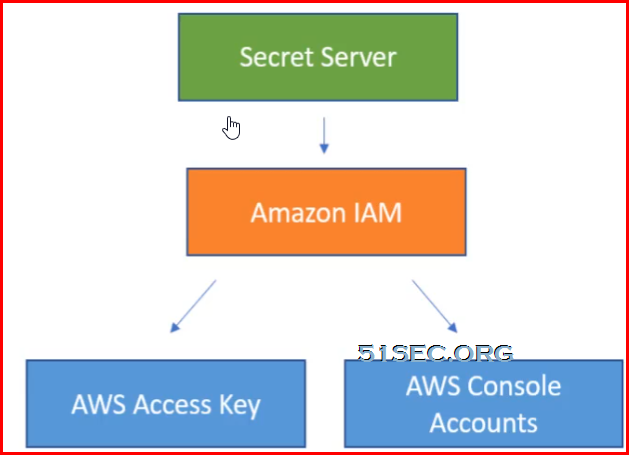
- Amazon Web services
- AWS accounts
- AWS access key
- AWS console account
- one secret using Amazon IAM secret template
- Amazon IAM access key permissions
- Iam:ListUsers
- Iam:GetLoginProfile
- Iam:ListAccessKeys
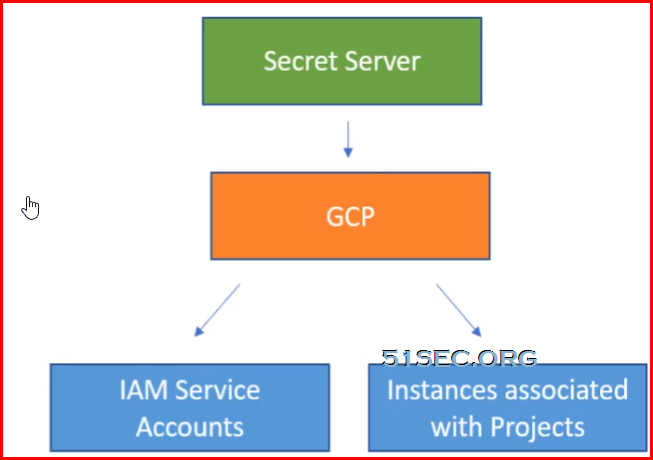
- Google Cloud platform
- Discovery and password changing of IAM service account users
- Discovery of instances associated to the projects
- Heartbeat and password changing of GCP service accounts
- Token rotation for GCP service accounts
Custom (Extensible)
- Anything - leverages PowerShell scripts
- SQL accounts & DB links
- Networking equipment
- Embedded password
Accounts Discovery Flow Charts
AD accounts discovery flow chart:
Unix/Linux accounts discovery flow chart:
Vmware ESX/ESXi accounts discovery flow chart:
AWS accounts discovery flow chart:
GCP accounts discovery flow chart:
Steps to Use Discovery
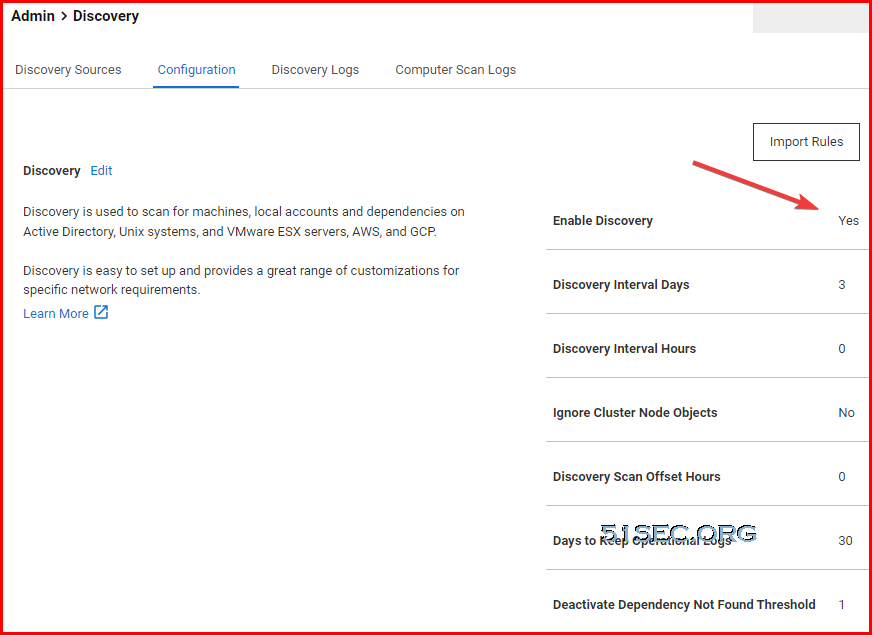
3 Add Discovery Sources and Rules
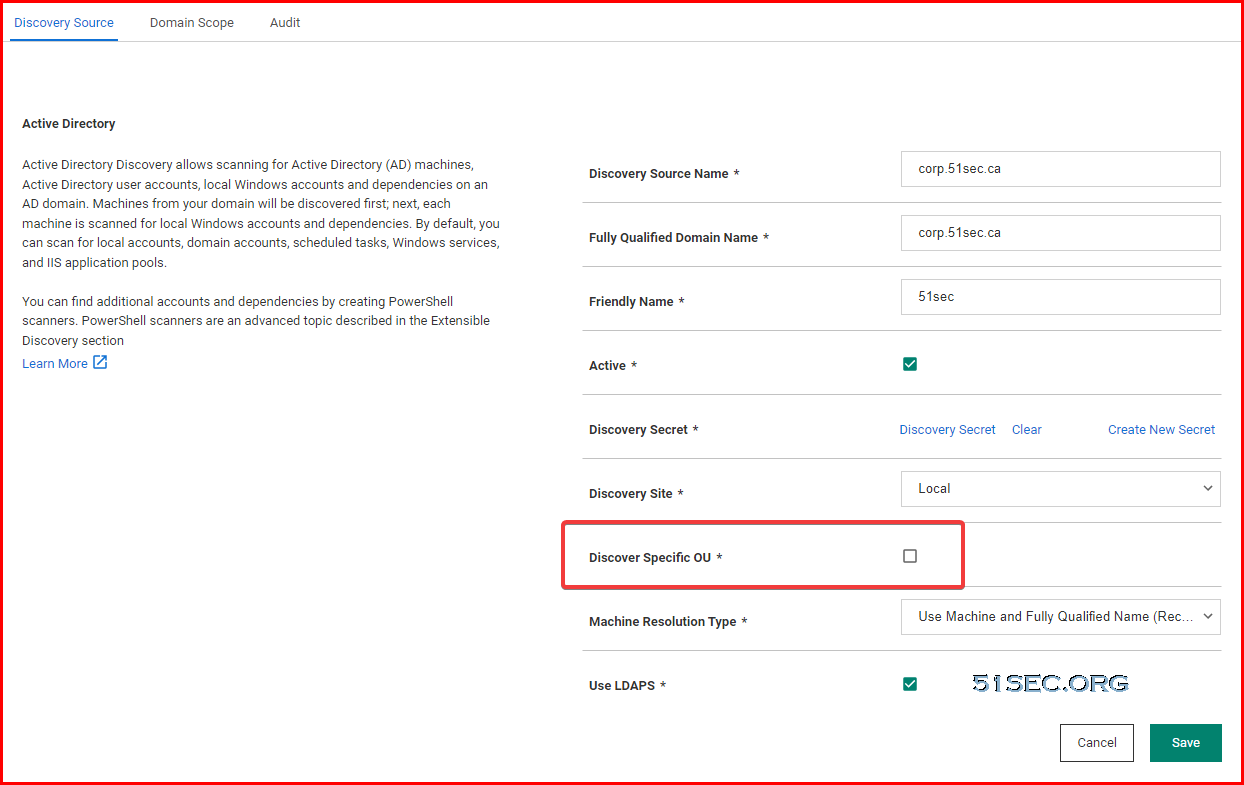
Active Directory Discovery Setting
Note: If Discover Specific OU enabled, you will need to define Domain Scope in the next tab. The domain scope is for OU, not CN. Once a parent OU added in, all child OUs are included into discovery as well.
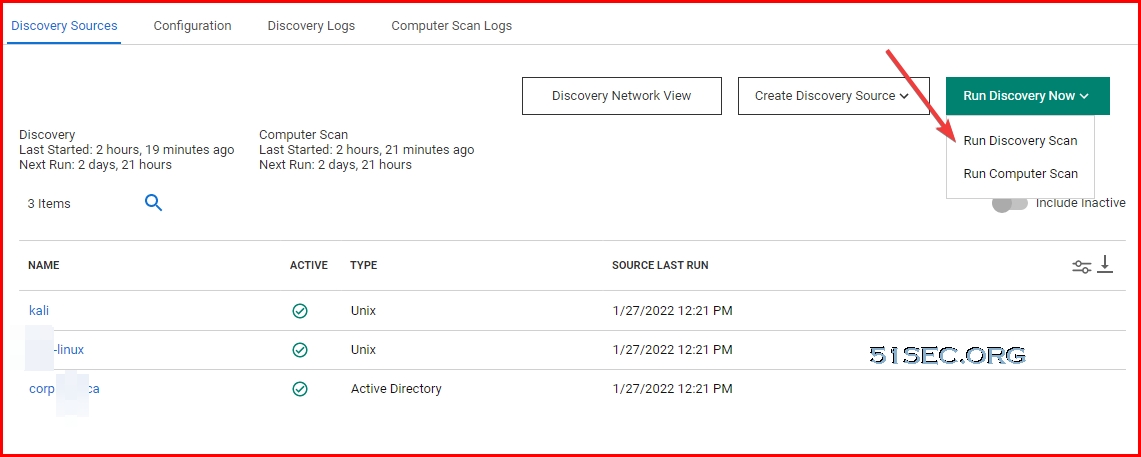
4 Run Discovery
5 Import Accounts
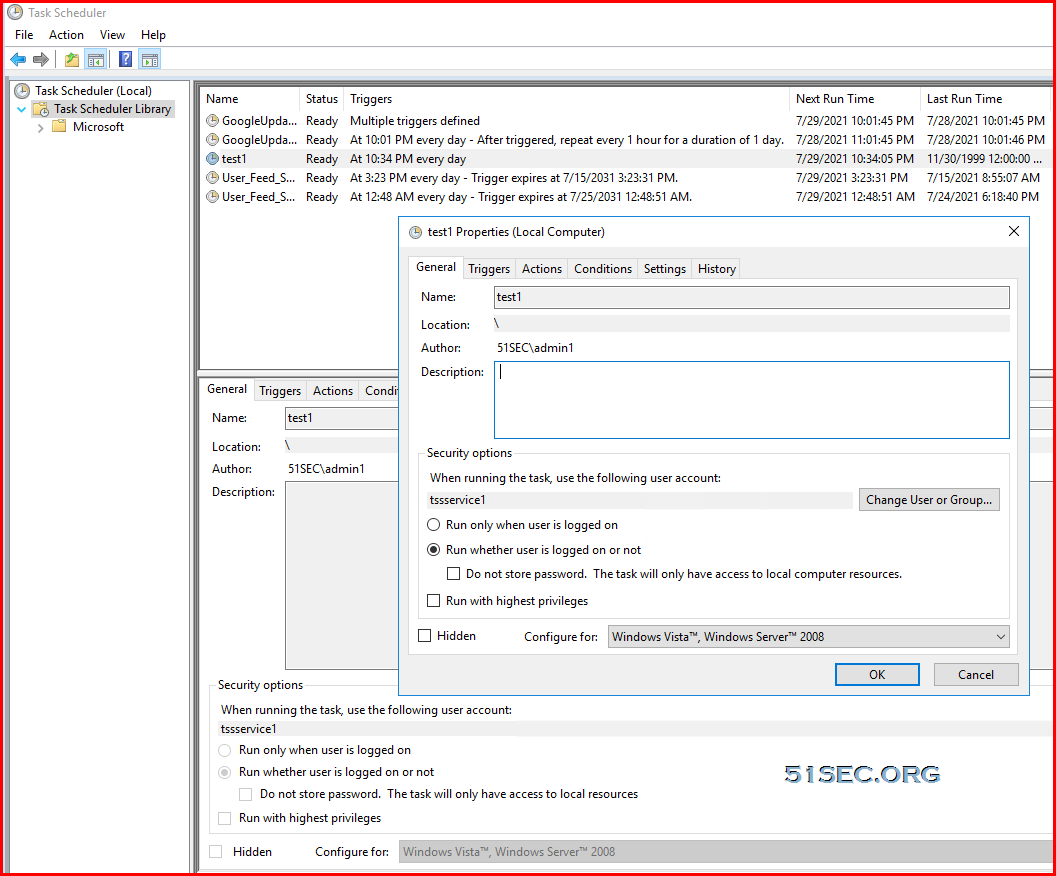
Set up a scheduled task to test service account
Troubleshooting - Discovery
Identify the issue(s):
- Discovery logs: admin -> Discovery -> Discovery logs and Computer Scan logs
- System logs: admin -> system logs
- Distributed Engine Logs: C:\Program Files -> Thycotic Software Ltd -> Distributed Engine -> Log -> SSDE file -> at the bottom of the file
Find the solution(s):
- Review the account running engine service
- Confirm the account has the appropriate permissions
- Compare this account to the account be used for discovery
Note:
Scanning Account's Permission:
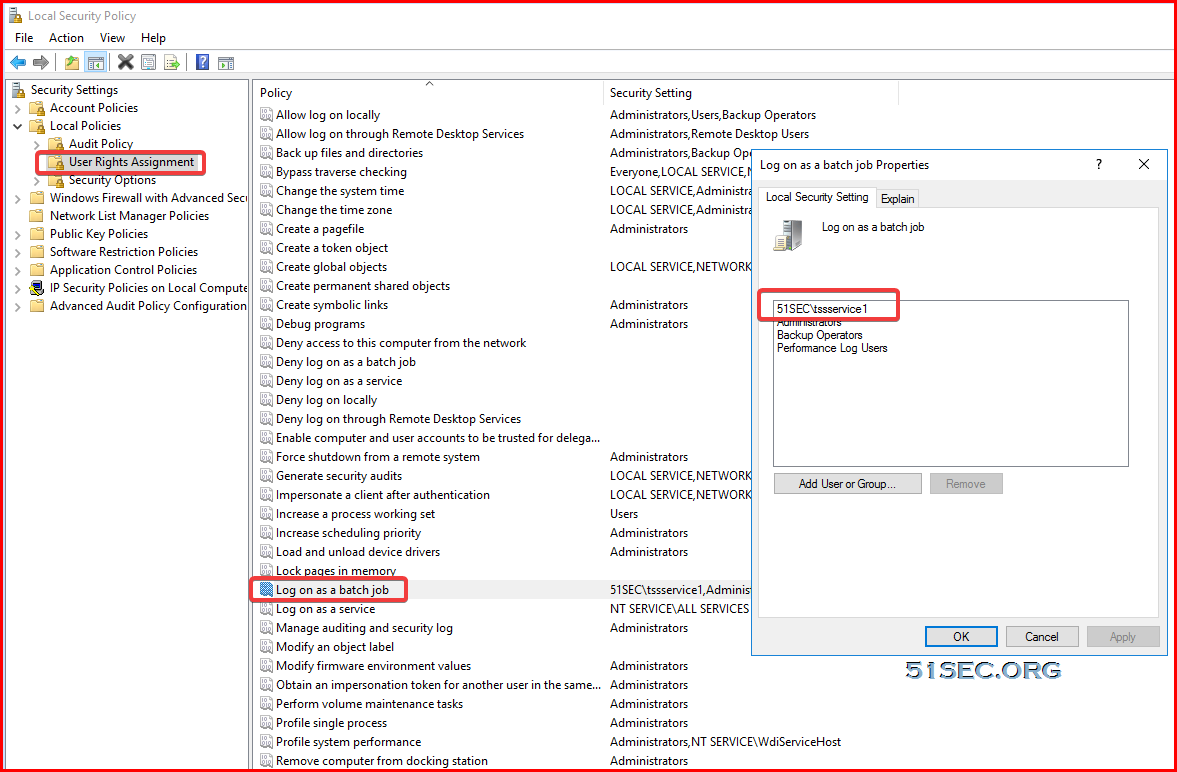
- Make the account e able to log on as service
- Grant the account read, write, and execute privileges to the entire distributed engine install directory and sub-folders
- Add the account to the administrators group on each computer that will be scanned
- same account as you run Distributed Engine Service.
Example: Error!
Exception: Retrieving the COM class factory for remote component with CLISID from <machine> failed due to error: 80070005
Filter Discover Report
Show a report to see all unmanaged accounts:
/* Domain accounts discovered in Secret Server that are not managed in Secret Server */
/* To filter the results to only a specific OU, uncomment out the
AND ou.Path = 'SpecificOU\SpecificOU'
line and change SpecificOU\SpecificOU to the folder path for the OU to filter */
/* To include a specific OU and its sub-OUs, uncomment out the AND ou.Path line
and edit it to
AND ou.Path CONTAINS 'SpecificOU\SpecificOU'
and change SpecificOU\SpecificOU to the folder path for the OU to filter */
SELECT
isnull(Domain,ds.Name) AS 'Discovery Source / Domain'
,ou.Path
,ca.AccountName AS 'Account Name'
FROM tbComputerAccount ca
INNER JOIN tbDiscoverySource ds on ca.DiscoverySourceId = ds.DiscoverySourceId
LEFT JOIN tbDomain d ON d.DomainId = ds.DomainId
LEFT JOIN tbOrganizationUnit ou ON ou.OrganizationUnitId = ca.OrganizationUnitId
LEFT JOIN tbSecret s ON s.ComputerAccountId = ca.ComputerAccountId
WHERE ds.Active = 1
AND ((d.EnableDiscovery is null) OR (d.EnableDiscovery = 1))
AND s.ComputerAccountId IS NULL
AND ca.OrganizationUnitId IS NOT NULL
/* AND ou.Path = 'SpecificOU\SpecificOU' */
GROUP BY isnull(Domain,ds.Name), ou.Path, ca.AccountName
HAVING COUNT(ca.AccountName) > 0
ORDER BY
1,2,3 ASC
SELECT
tc.DiscoverySourceId AS 'DiscoverySourceId',
tds.Name AS 'DiscoverySourceName',
tca.AccountName AS 'Account',
tc.ComputerName AS 'Host Name',
CONVERT(VARCHAR(20),tc.LastPolledDate,107) AS 'Last Scanned'
FROM
tbComputer tc
JOIN tbComputerAccount tca
ON tc.ComputerId=tca.ComputerId
JOIN tbDiscoverySource tds
on tc.DiscoverySourceId=tds.DiscoverySourceId
LEFT JOIN tbSecret ts
ON ts.ComputerAccountId = tca.ComputerAccountId
WHERE ts.ComputerAccountId IS NULL
ORDER BY tca.AccountName asc







No comments:
Post a Comment