This post is to sum up the steps using netboot.xyz package to install Linux system into Oracle Free Tier machine, either x86 or ARM architecture.
Create Your Oracle VM and create local vnc console
- Oracle Cloud VPS VNC Console Connection
- Run Free Arm-based Oracle Linux (Install Docker/Docker Compose/Portainer/Ubuntu Virtual Desktop)
- Install BT (aaPanel) in Oracle ARM-based Virtual Instance with Oracle Linux 8
- Install xRDP with Ubuntu Desktop on Oracle ARM VM ( xRDP Sound Support)
- DD Original Ubuntu Image to Oracle ARM VM and Install Lxde desktop and xRDP with Sound Forwarding
- DD Windows OS to Cloud Linux VM (Oracle /GCP /Azure)
- Enable IPv6 on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure & Asiign it to CentOS
- Oracle Cloud Platform (OCP) Tips and Tricks
Download netboot.efi
Download netboot.efi file.- x86_64:https://boot.netboot.xyz/ipxe/netboot.xyz.efi
- arm64:https://boot.netboot.xyz/ipxe/netboot.xyz-arm64.efi
root@ubuntu-arm-test:~# cd /boot/efi
root@ubuntu-arm-test:/boot/efi# wget https://boot.netboot.xyz/ipxe/netboot.xyz-arm64.efi^C
root@ubuntu-arm-test:/boot/efi#
root@ubuntu-arm-test:/boot/efi# ls
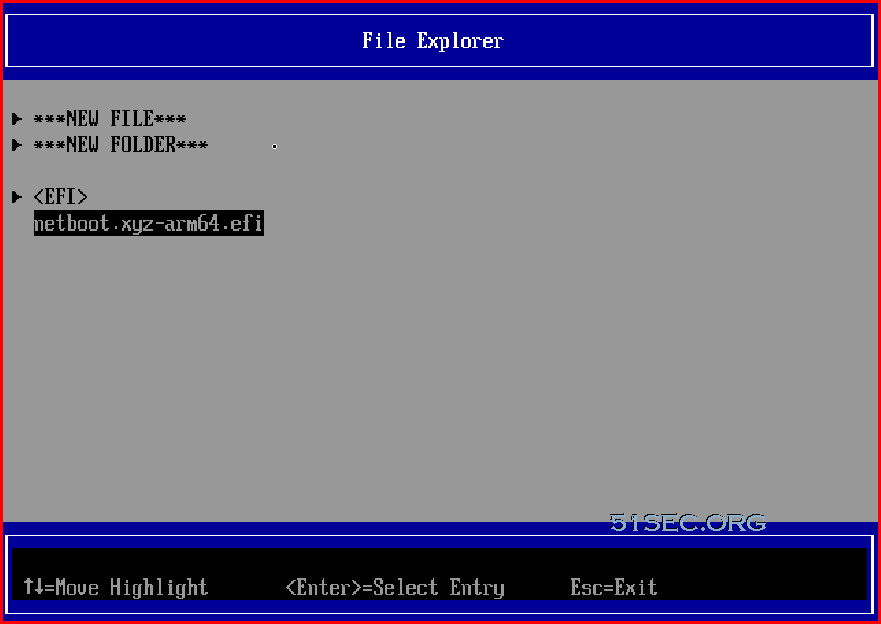
EFI netboot.xyz-arm64.efi
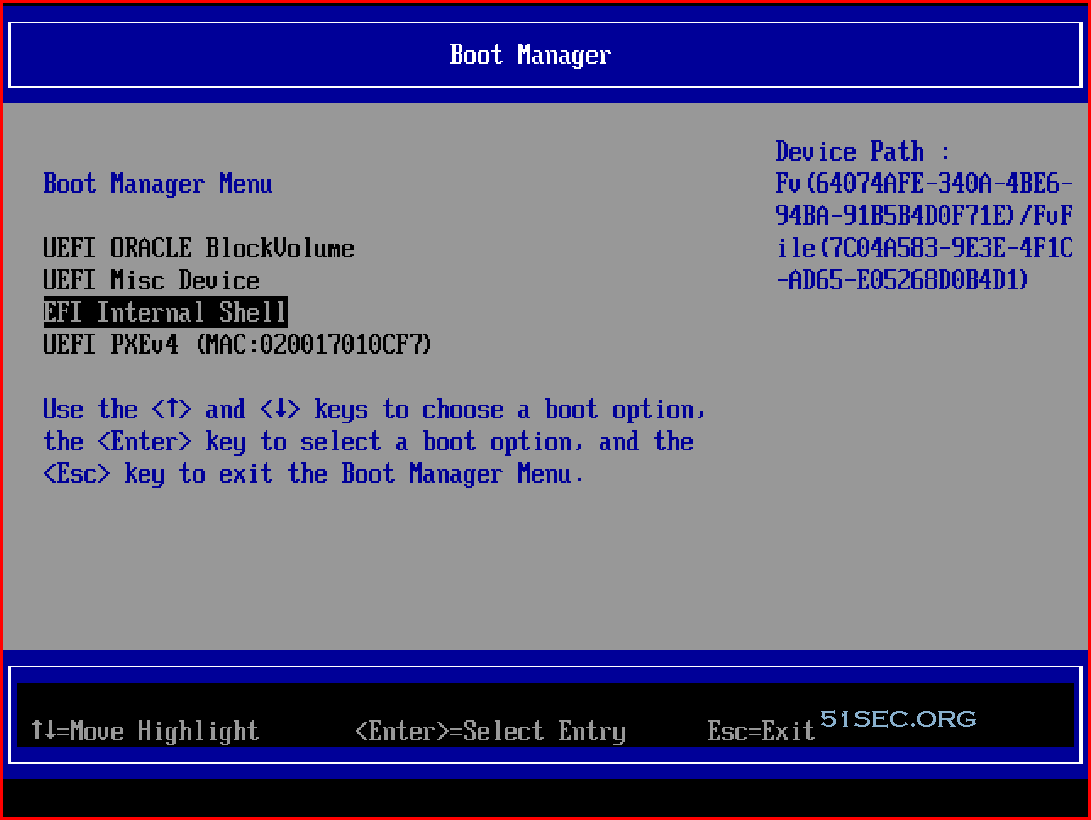
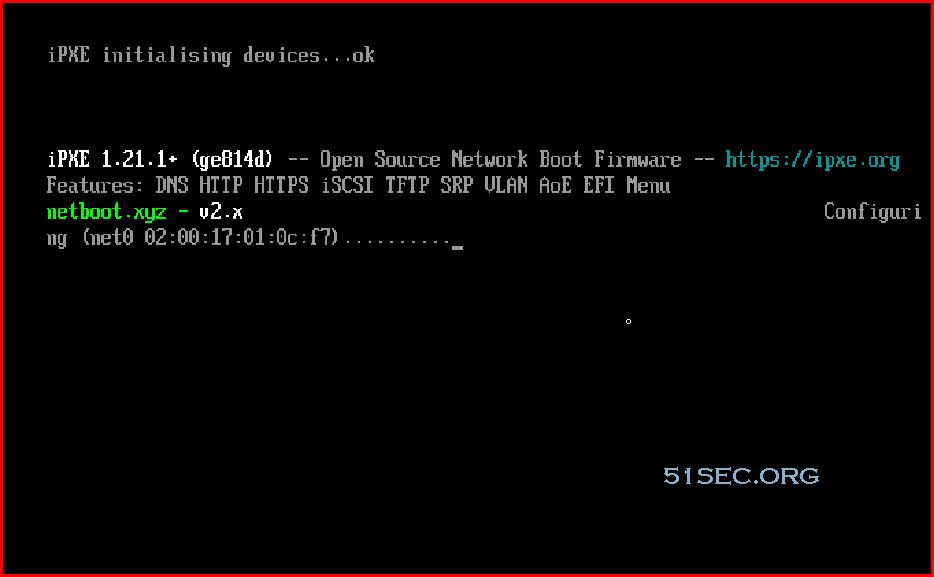
Enter into BIOS and Run netboot.xyz arm64 efi file
Using up/down arrow key to move your selection to Boot Manager then Enter
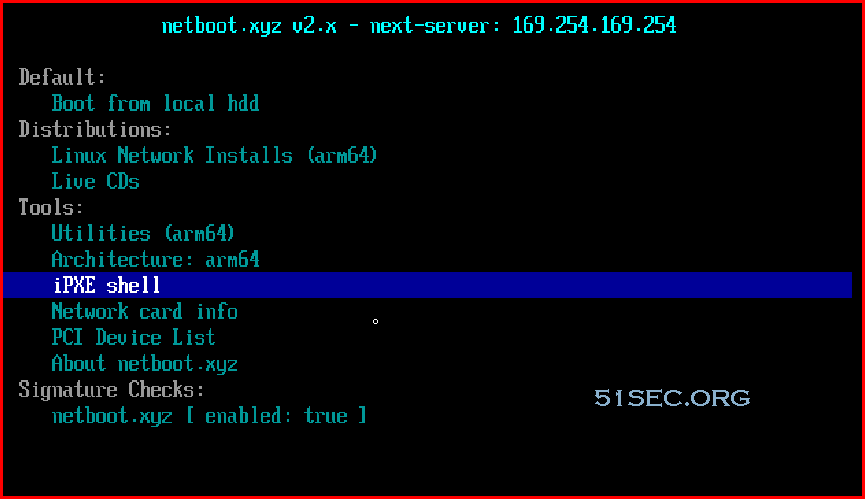
Choose EFT Internal Shell
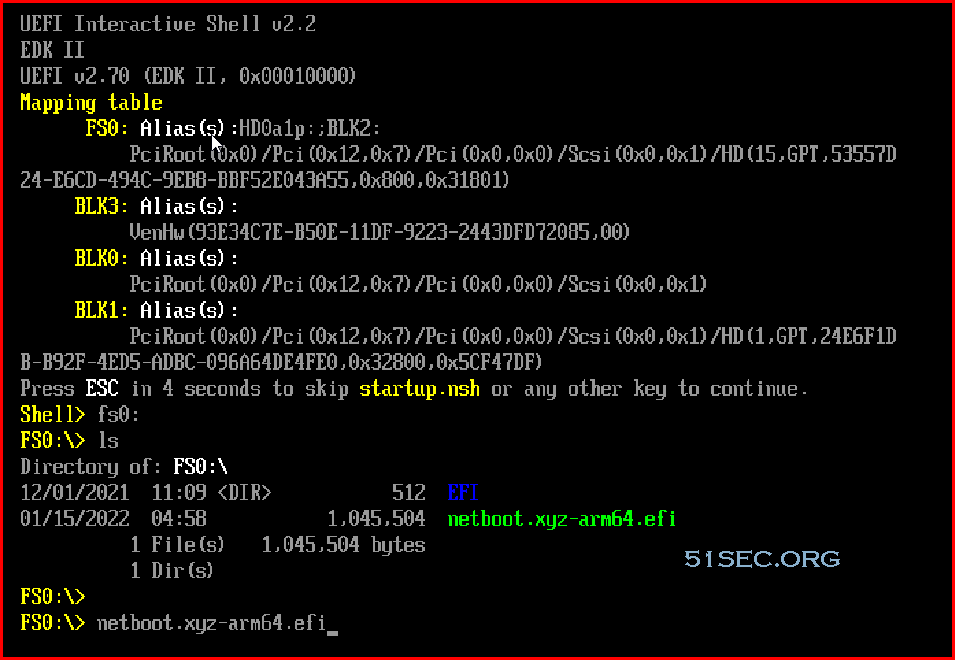
Press ESC key to skip startup.nsh, you will get into Shell>
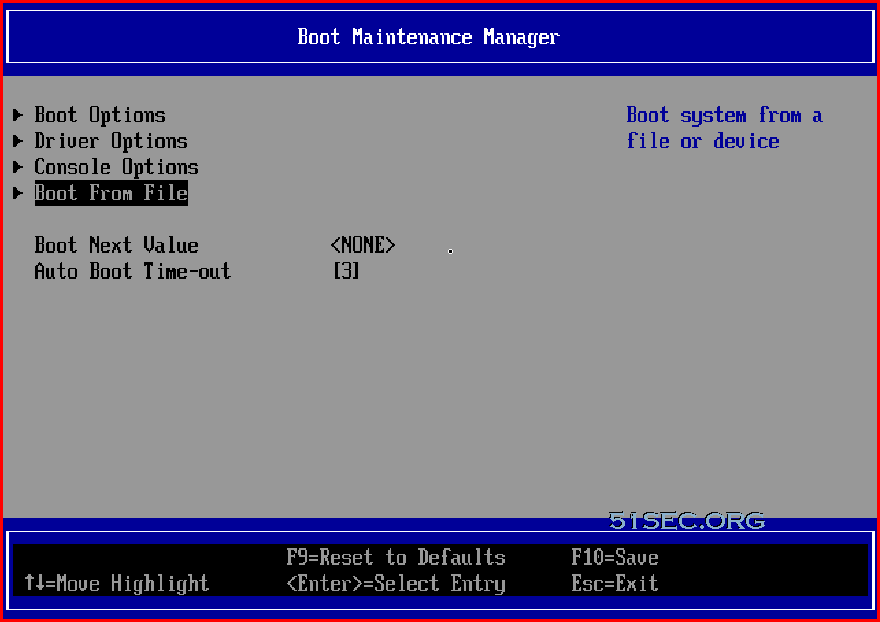
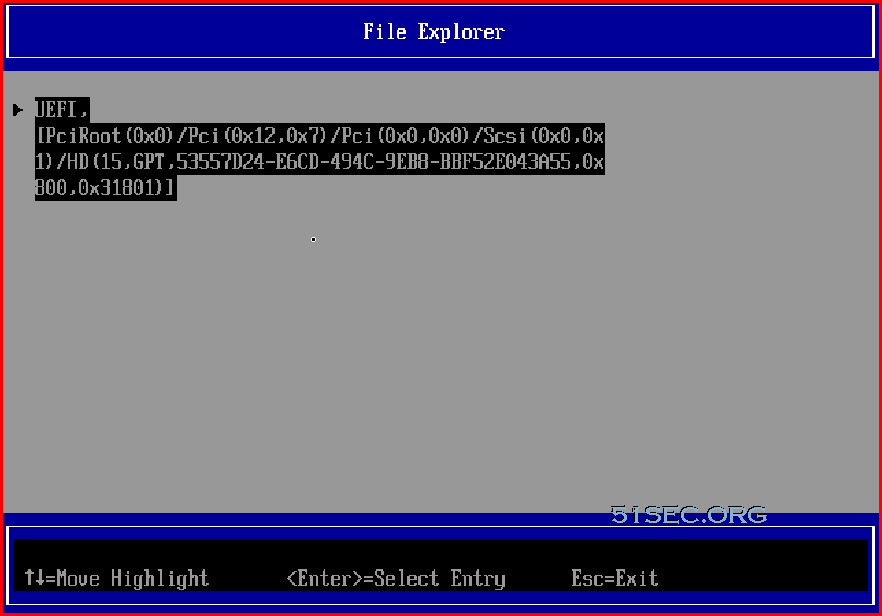
Or you can boot EFI from Boot Maintenance Manager - Boot From File
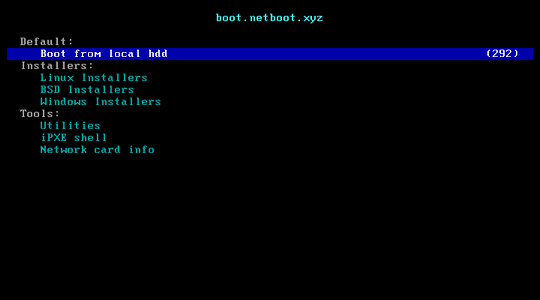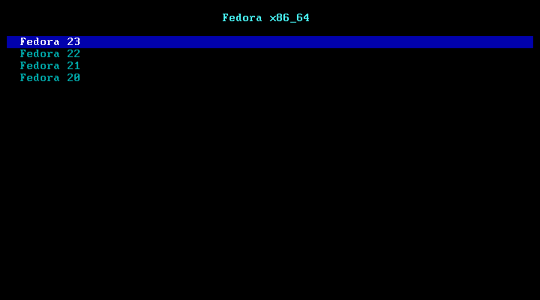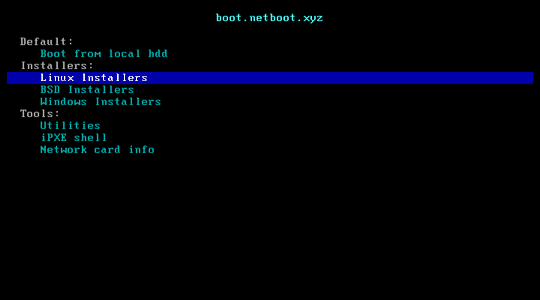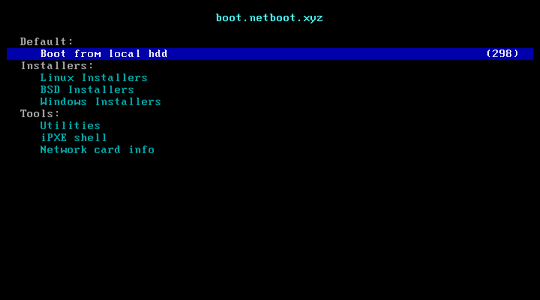
iPXE Shell
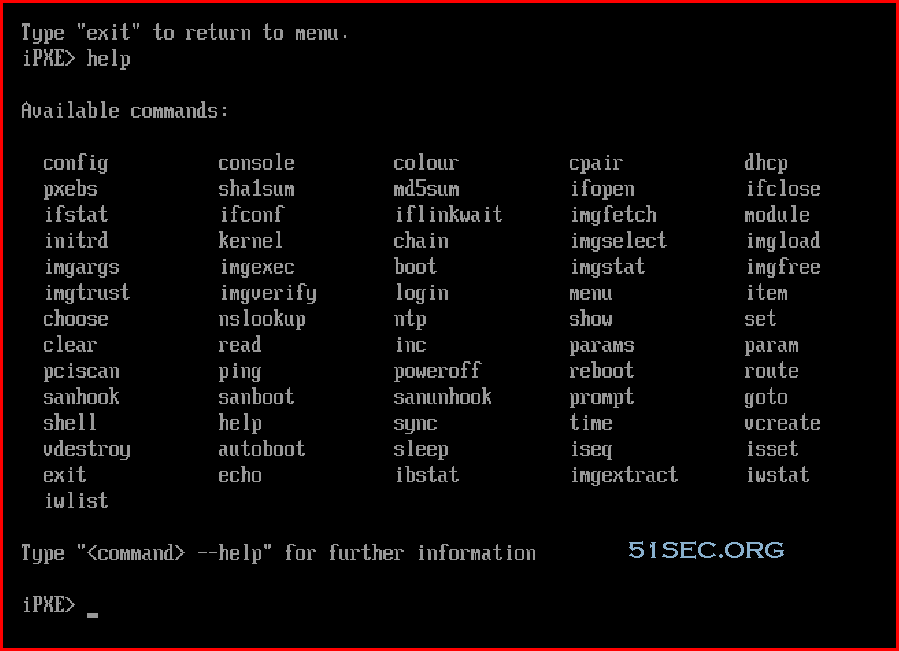
After started netboot.xyz, you an run iPXE shell:
Some common commands of ipxe shell
chain、dhcp、kernel、initrd、config、sanboot、autoboot、set、boot、goto
You can add after the corresponding command to --help get more help for the command, go and try it.
- If ARM uses netboot.xyz to install CentOS, the kernel will not be downloaded. Just download it manually;
- x86_64 CentOS cannot install a version greater than 7.2 because of insufficient memory.
Load Disk and Boot manually
shift+pageUp/pageDown. You can exit (leave the shell and exit to the EFI management interface) or reboot.To load the disk and boot manually:
Shell>FS0:
FS0:\> ls
Directory of: FS0:\
09/22/2019 19:43 <DIR> 4,096 EFI
04/15/2020 20:51 10,668 NvVars
1 File(s) 10,668 bytes
1 Dir(s)
FS0:\> cd EFI
FS0:\EFI\> cd debian
FS0:\EFI\debian\> grub64.efi
EFI Shell Cheat-sheet
The map command print the discovered partition and device mapping (akin lsblk), vol <VOL-NAME> print more details.
List boot options:
FS0:\> bcfg boot dump -b
...
Option: 06. Variable: Boot0004
Desc - UEFI QEMU HARDDISK QM00001
DevPath - PciRoot(0x0)/Pci(0x1,0x1)/Ata(0x0)
Optional- Y
...
Change boot order (shift down all other options)
# move option 6 to position 0, shifting down the others
FS0:\> bcfg boot mv 6 0
Remove an option
FS0:\> bcfg boot rm 4
Add an option
FS0:\> bcfg boot add 1 FS0:\EFI\GRUB\grubx64.efi "GRUB"
Target = 0007.
bcfg: Add Boot0007 as 1
help output, more readable than on a small console:
FS0:\> cat help.txt
alias - Displays, creates, or deletes UEFI Shell aliases.
attrib - Displays or modifies the attributes of files or directories.
bcfg - Manages the boot and driver options that are stored in NVRAM.
cd - Displays or changes the current directory.
cls - Clears the console output and optionally changes the background and foreground color.
comp - Compares the contents of two files on a byte-for-byte basis.
connect - Binds a driver to a specific device and starts the driver.
cp - Copies one or more files or directories to another location.
date - Displays and sets the current date for the system.
dblk - Displays one or more blocks from a block device.
devices - Displays the list of devices managed by UEFI drivers.
devtree - Displays the UEFI Driver Model compliant device tree.
dh - Displays the device handles in the UEFI environment.
disconnect - Disconnects one or more drivers from the specified devices.
dmem - Displays the contents of system or device memory.
dmpstore - Manages all UEFI variables.
drivers - Displays the UEFI driver list.
drvcfg - Invokes the driver configuration.
drvdiag - Invokes the Driver Diagnostics Protocol.
echo - Controls script file command echoing or displays a message.
edit - Provides a full screen text editor for ASCII or UCS-2 files.
eficompress - Compresses a file using UEFI Compression Algorithm.
efidecompress - Decompresses a file using UEFI Decompression Algorithm.
else - Identifies the code executed when 'if' is FALSE.
endfor - Ends a 'for' loop.
endif - Ends the block of a script controlled by an 'if' statement.
exit - Exits the UEFI Shell or the current script.
for - Starts a loop based on 'for' syntax.
getmtc - Gets the MTC from BootServices and displays it.
goto - Moves around the point of execution in a script.
help - Displays the UEFI Shell command list or verbose command help.
hexedit - Provides a full screen hex editor for files, block devices, or memory.
if - Executes commands in specified conditions.
ifconfig - Modifies the default IP address of the UEFI IPv4 Network Stack.
ifconfig6 - Displays or modifies IPv6 configuration for network interface.
load - Loads a UEFI driver into memory.
loadpcirom - Loads a PCI Option ROM.
ls - Lists the contents of a directory or file information.
map - Displays or defines file system mappings.
memmap - Displays the memory map maintained by the UEFI environment.
mkdir - Creates one or more new directories.
mm - Displays or modifies MEM/MMIO/IO/PCI/PCIE address space.
mode - Displays or changes the console output device mode.
mv - Moves one or more files to a destination within or between file systems.
openinfo - Displays the protocols and agents associated with a handle.
parse - Retrieves a value from a standard format output file.
pause - Pauses a script and waits for an operator to press a key.
pci - Displays PCI device list or PCI function configuration space and PCIe extended
configuration space.
ping - Ping the target host with an IPv4 stack.
ping6 - Ping a target machine with UEFI IPv6 network stack.
reconnect - Reconnects drivers to the specific device.
reset - Resets the system.
rm - Deletes one or more files or directories.
sermode - Sets serial port attributes.
set - Displays or modifies UEFI Shell environment variables.
setsize - Adjusts the size of a file.
setvar - Displays or modifies a UEFI variable.
shift - Shifts in-script parameter positions.
smbiosview - Displays SMBIOS information.
stall - Stalls the operation for a specified number of microseconds.
time - Displays or sets the current time for the system.
timezone - Displays or sets time zone information.
touch - Updates the filename timestamp with the current system date and time.
type - Sends the contents of a file to the standard output device.
unload - Unloads a driver image that was already loaded.
ver - Displays UEFI Firmware version information.
vol - Displays or modifies information about a disk volume.
Help usage:help [cmd|pattern|special] [-usage] [-verbose] [-section name][-b]
Reference: GRUB/EFI examples from the Archlinux Wiki









No comments:
Post a Comment